-
0 引言
-
韧性剪切带在造山带以及大陆内部变形中起着关键和重要的作用,它们协调了剪切带两侧地质体的相对运动,是吸收大陆变形的重要方式,因此成为板块构造解释板块内部变形的重要依据 (sengör et al.,2019),同时韧性剪切带也是大陆内部应变集中的地区,构成了从露头尺度到超大陆尺度的强应变带,这些应变带又成为地壳甚至岩石圈中主要的薄弱带,在后期的演化中往往成为控制后期变形的重要构造带。韧性剪切带的研究也因此是构造地质领域长期探索的方向。剪切带的形成会遵循一定的规律,形成一定的空间结构。一般而言,韧性剪切带由网状分布的次一级剪切带以及它们围限的弱变形域构成(Fossen and Cavalcante, 2017)。而多条有相似性质、相同构造背景的剪切带则可以组成更高级的韧性变形系统,构成了造山带规模的巨型变形构造,成为大陆变形中重要的表现形式(Marshak et al.,2003; Storti et al.,2003; Cunningham,2007,2013;Mann,2007)。沿着造山带发育的韧性剪切带已取得很多研究共识,但是它们的作用、机制以及背景在不同时代和不同类型造山带中存在巨大差别。韧性剪切带或剪切系统强烈地改造了造山带的原始结构,造成了构造带或构造单元的缺失或者重复,给恢复造山带原始结构和洋陆演化造成了困难,因此在造山带中识别韧性剪切带和剪切系统,恢复其组成和形成过程及其位移量是造山带研究的重要内容。
-
走滑双重构造成为近年来构造地质的重要研究领域,在不同造山带中都有发现(Corsini et al., 1996;Yang et al.,2020; Neves et al.,2021),甚至在水星上也识别出类似的变形(Kumar,2005),它们的形成往往与岩石圈流变学特征、造山带组成和类型等因素有关(Corsini et al.,1996;Neves et al., 2021)。中亚造山带是规模最大的显生宙增生型造山带,韧性变形在该造山带的演化过程中起到了重要作用,不同的学者已经开展了很多工作(Zhang et al.,2022a 及所引文献),最近笔者在该造山带中段的阿拉善地区发现了一个大型的走滑双重构造,并对这个双重构造的内部主要组成开展了研究 (Zhang et al.,2021a; Zhao et al.,2022),但是对其中的一些组成单元的时代和性质还不清楚,也缺少一些剪切带位移量的估算,对控制该双重构造的因素、形成背景以及它在整个造山带中的作用也不清楚,本文在前期工作的基础上,补充了一些剪切带的新资料,分析了该双重构造形成的控制因素,限定了该双重构造的位移量,并讨论了它在重要造山带演化中起到的作用。
-
1 地质背景
-
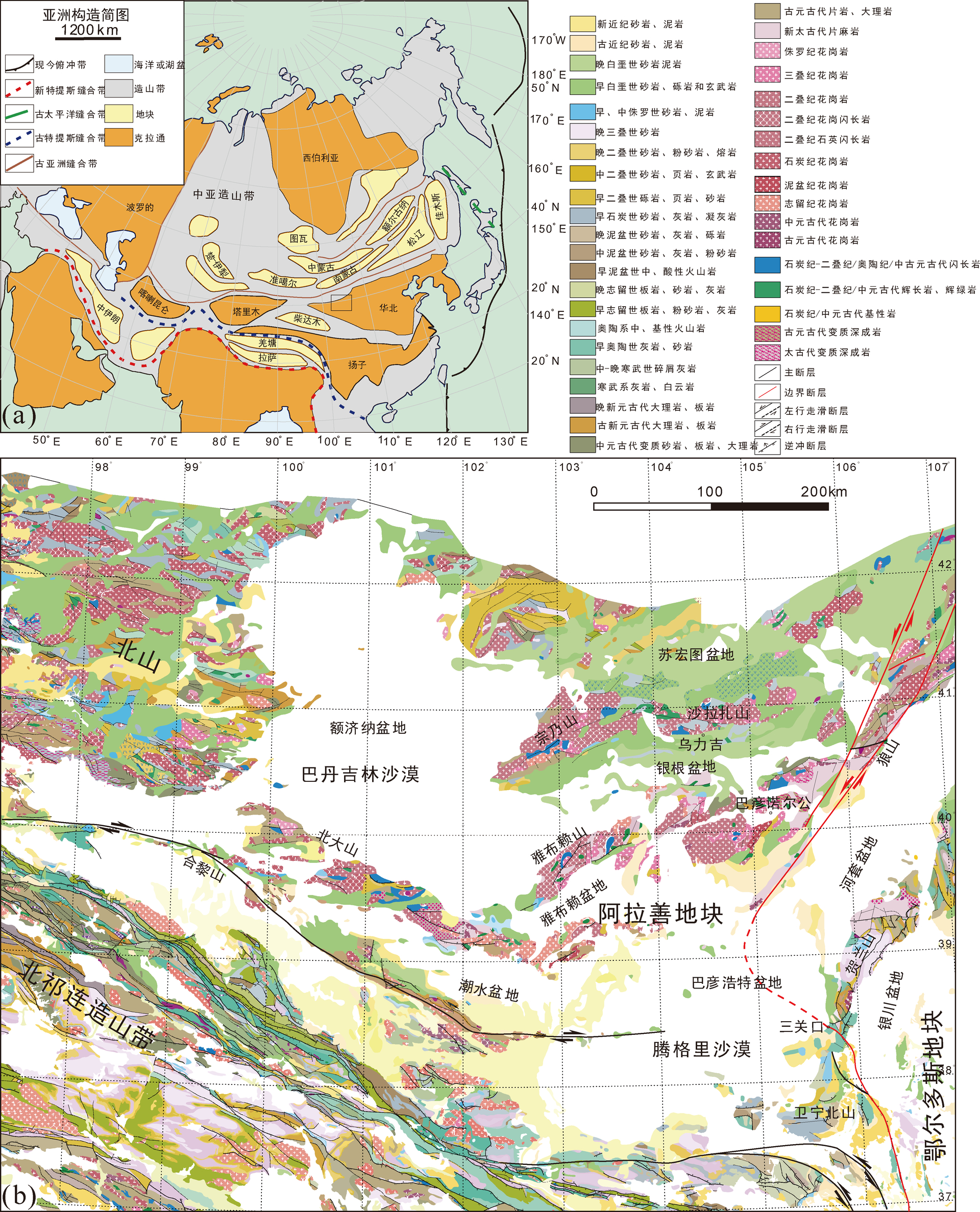
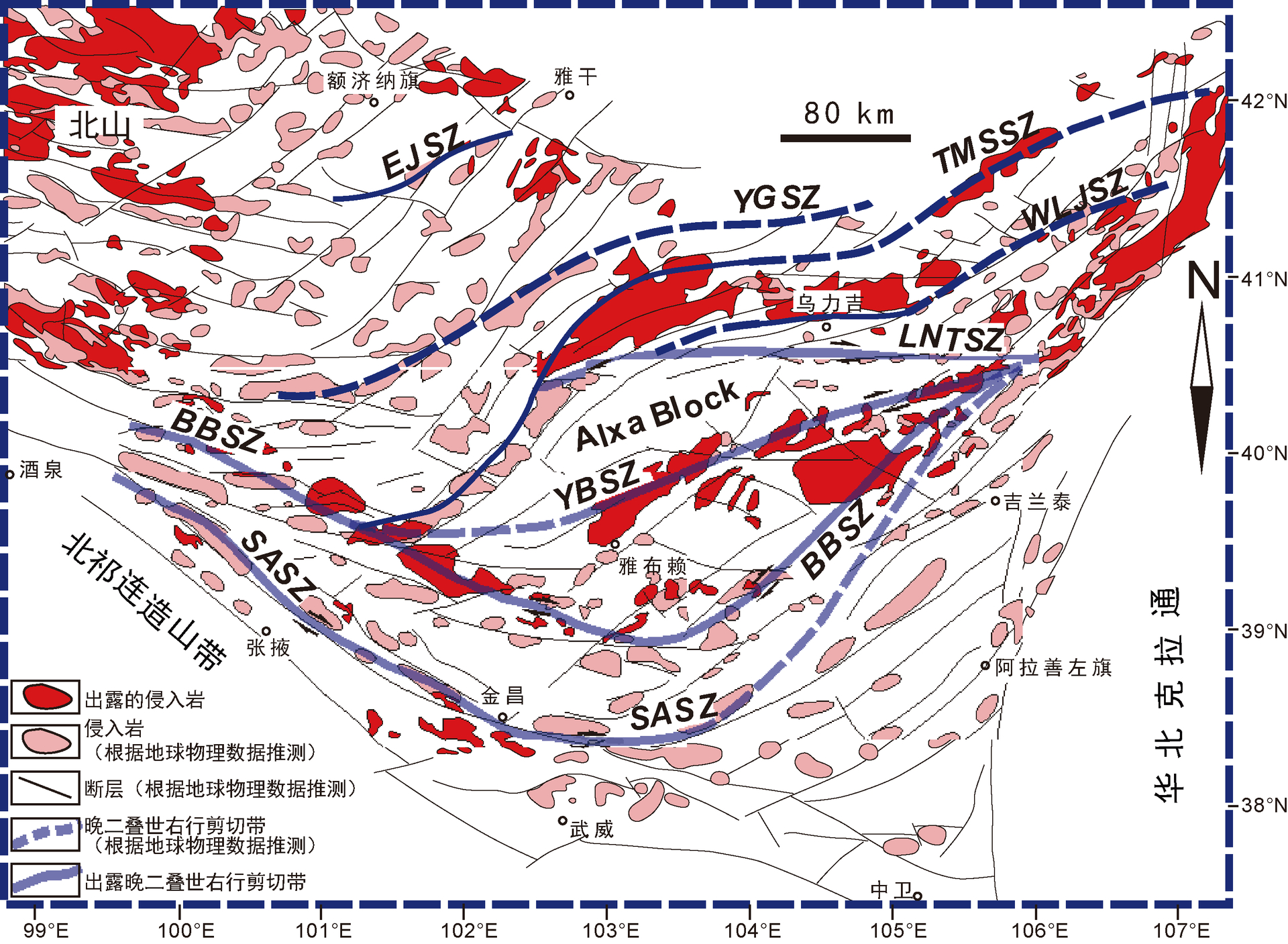
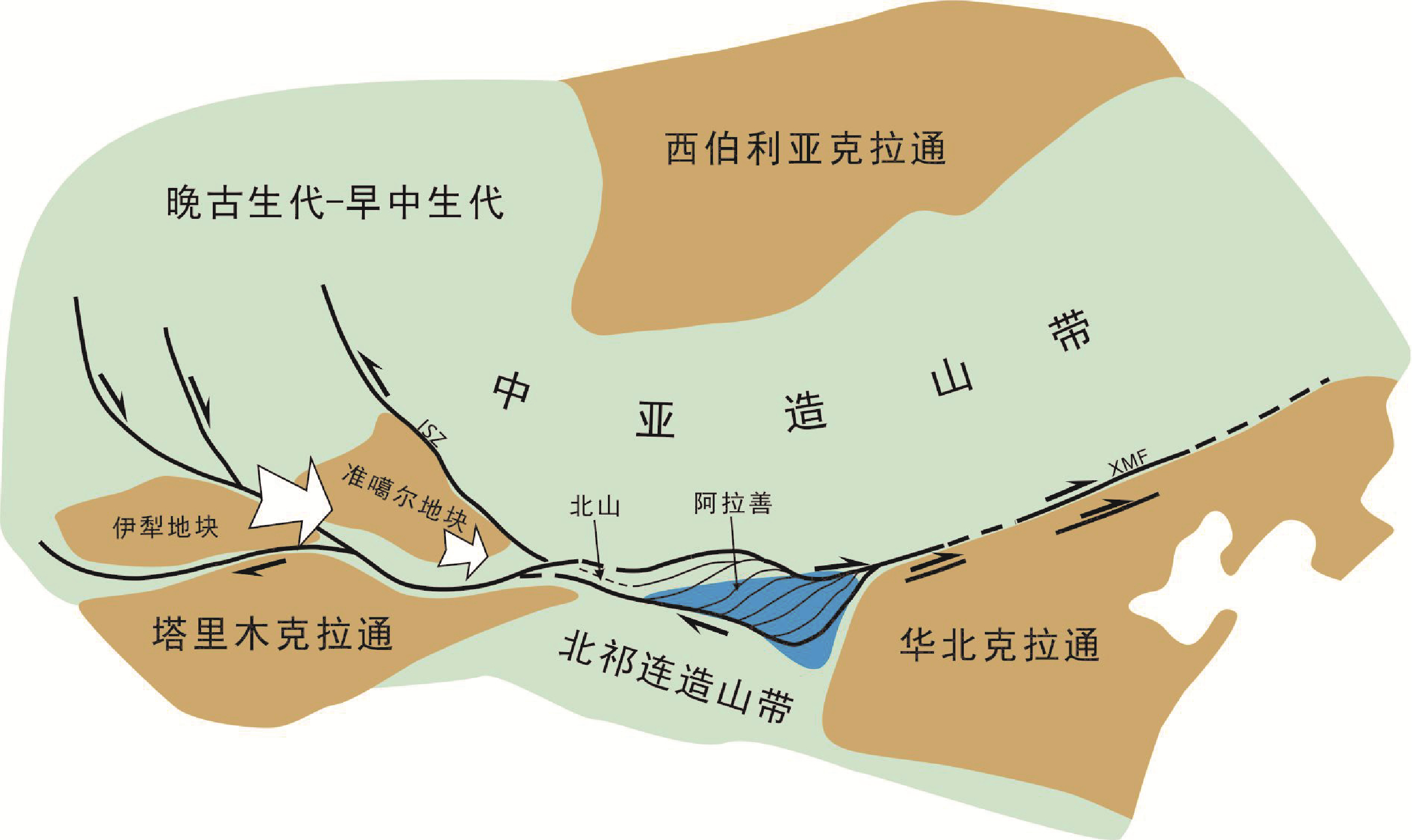
中亚造山带(CAOB)整体位于华北、塔里木、西伯利亚、波罗的等几个克拉通之间,是一个新元古代—三叠纪发育的增生型造山带,虽然不同的学者定义和范围不完全一样,但都认为该造山带是地球上显生宙期间规模最大的增生型造山带(Sengör et al.,1993,2018;Sengör and Natalin,1996; Jahn, 2004;Xiao et al.,2009,2015)。阿拉善地块或构造带位于该造山带中段的南侧,是一个与古亚洲洋演化息息相关的地质单元(Zheng et al.,2014,2019a, b,2022; Liu et al.,2017a, b,2019a, b; Song et al.,2018; Hui et al.,2021;Zhang et al.,2021b)。阿拉善地块西侧为北山造山带,东侧为华北克拉通 (图1)。传统上被认为是一个前寒武纪块体,属于华北克拉通的一部分。其范围从北侧的恩格尔乌苏蛇绿混杂岩带到南侧的河西走廊北缘。近来的研究表明阿拉善内部并非一个稳定的块体,而是被多条蛇绿岩和众多方向的韧性剪切带分割,主体构造走向为近东西向(Zhang et al.,2013a,2022a; Song et al.,2020)。随着研究的深入,阿拉善北缘边界被认为是查干楚鲁蛇绿岩带而不是北侧的恩格尔乌苏蛇绿岩带(Zhang et al.,2015a)。阿拉善内部前寒武纪出露地区主要集中在南缘龙首山— 北大山—巴彦乌拉山—狼山一带(Zhang et al., 2013b;牛鹏飞等,2022; Niu et al.,2022),北侧和中部地区大量出露晚古生代早—中二叠世花岗质岩体,多呈近东西向带状分布,它们与北侧的古亚洲洋演化以及中亚造山带形成具有密切的关系 (Zhang et al.,2015a;Zheng et al.,2019a,b,2022; Hui et al.,2021)。本文介绍的韧性剪切系统,多数发育于这些晚古生代的侵入岩之中,它们之间可能有一定的成因联系(图2)。随着古亚洲洋在该地区的最终闭合,阿拉善进入陆内演化阶段,内部发育了多期次的挤压—拉伸活动以及内部的韧性走滑,形成了大量中、新生代的盆地,如潮水盆地、银根— 额济纳盆地、雅布赖盆地等。
-
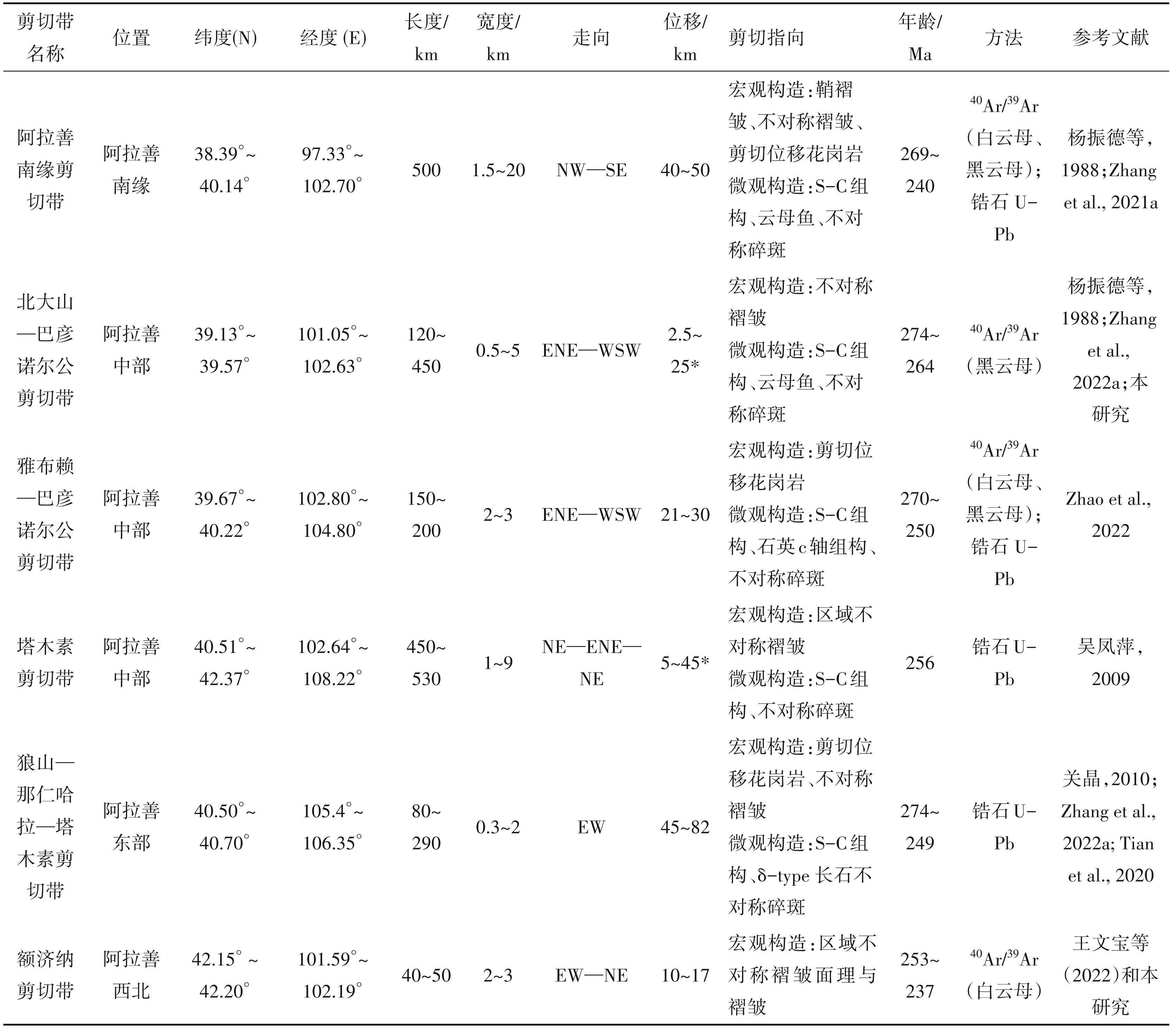
关于阿拉善地区的韧性剪切带,早年杨振德等 (1988)曾有报道,但受限于当时的条件,对剪切带的性质、年龄以及规模都没得到很好的限定,但为后期工作打下了基础。此后不同的学者在阿拉善不同地区及其邻近地区报道了一系列不同活动时代的韧性剪切带,如巴彦乌拉山—狼山剪切带 (Zhang et al.,2013a,2022a,b;公王斌等,2017)、英巴剪切带(Zhou et al.,2012)、雅布赖剪切带(王东升等,2016;Zhao et al.,2022)、龙首山剪切带 (Zhang et al.,2021a)、雅干变质核杂岩(Zheng et al.,1991; Zheng and Zhang,1994)、巴彦诺尔公剪切带(Feng et al.,2020)、北大山剪切带(宫江华等, 2018;Zhang et al.,2022a)、狼山—那仁哈拉—塔木素剪切带(吴凤萍,2009;关晶,2010;Zhang et al., 2022a,b)、额济纳剪切带(崔骁等,2019)、Zunnbayan 剪切带(Lamb et al.,1999;Webb et al.,2010)。目前对这些剪切带的研究主要还是在运动学性质的判定等工作上,对于这些剪切带的形成机制、空间关系、走滑位移、变形时代以及构造背景研究尚属薄弱(Zhang et al.,2022a,b)。例如巴彦诺尔公剪切带被认为是侏罗纪而非三叠纪(Feng et al., 2020);巴彦乌拉山—狼山剪切带被认为是泥盆纪晚期—石炭纪早期,而非三叠纪(公王斌等,2017)。最近,Zhang et al. (2022a)对这些剪切带做了一定的综述,但仍然缺少一些剪切带的具体活动时代和性质的判断,对于走滑位移的估算目前也还很少。在这些剪切带中,大多数为韧性右行剪切,而且活动时代基本都在 260~250 Ma(图2),然而它们目前分布并没有体现出一定的规律性,这种分布格局是原始的还是后期改造的仍没有得到解释。
-
图1 北山—阿拉善地区地质图
-
中亚造山带及研究区索引图(a)及阿拉善及邻区地质图(b)
-
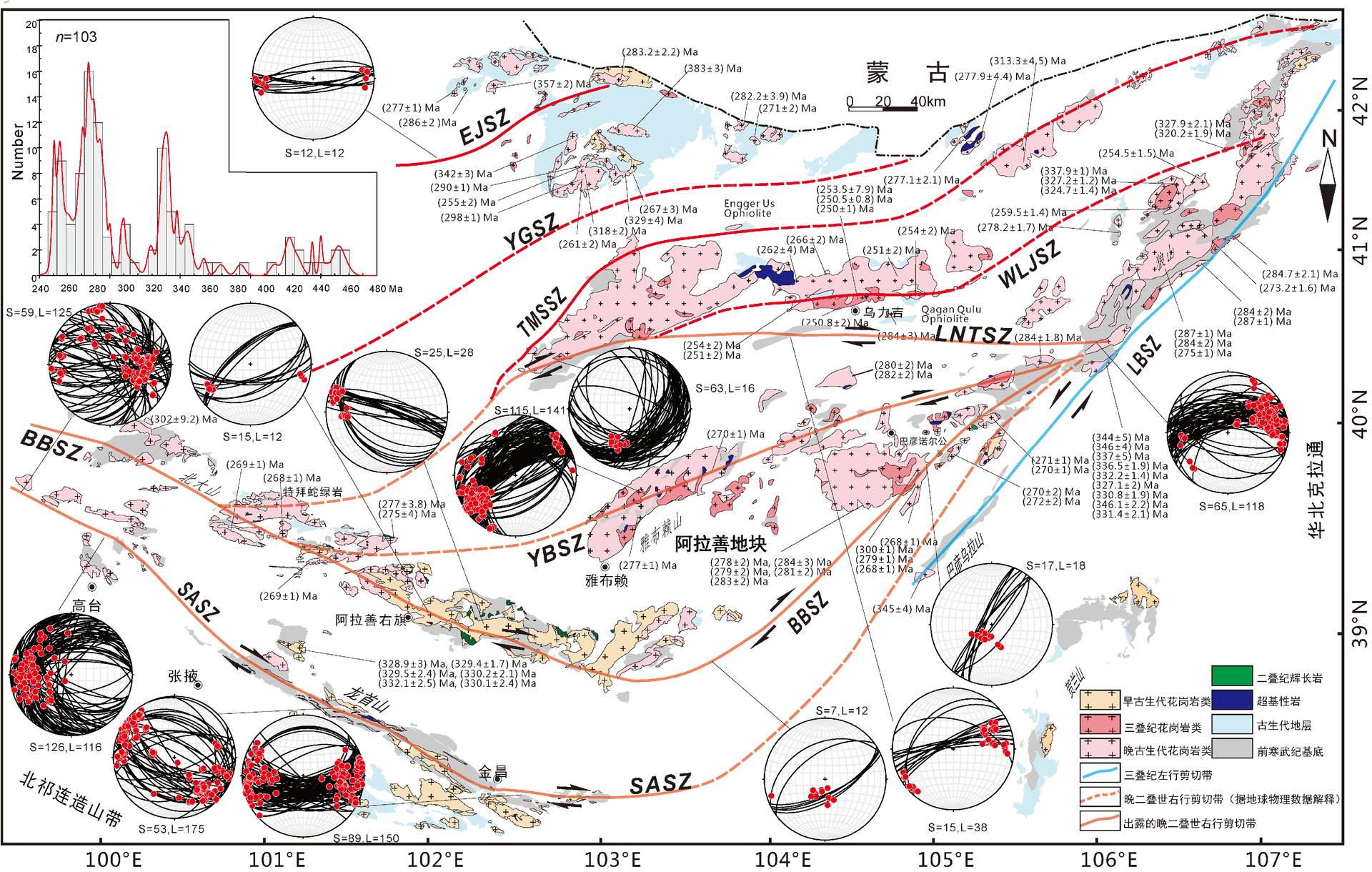
图2 阿拉善地区侵入岩分布、年龄、韧性剪切带及其产状赤平投影图
-
(年龄数据据赖新荣等,2007;韩宝福等,2010;冉皞等,2012;史兴俊等,2012,2020;张文等,2013;郑荣国等,2013; Dan et al.,2014,2015a,b,2016; Lin et al.,2014; Shi et al.,2014;张伟等,2014;Hu et al.,2015; Wang et al.,2015; Liu et al.,2016a,b; Zhang et al., 2016b; Liu et al.,2017a, b,2018; Xue et al.,2017; Zhang et al.,2017; Shi et al.,2018; Liu et al.,2019a,b; Zheng et al.,2019a,b; Li et al.,2020; Song et al.,2020; Zhao et al.,2020)
-
2 方法
-
本文主要基于阿拉善野外多个地区的大比例尺填图,填图面积超过 800 km2,比例尺一般为 1∶ 10000 或者 1∶50000。其中包括了 700 多个位置的面理和线理的产状测量。同时在野外采集定向标本用于室内的显微构造分析。
-
在填图过程中,针对不同剪切带,从不同尺度判别剪切带的运动学。在宏观尺度上可以在地图上确定剪切带的分布、宽度及其长度。一些地质单元的分布以及剪切带两侧单元之间的边界可以作为填图过程中确定运动学的标志。在中尺度上,剪切带中的许多不对称构造,如不对称褶皱、布丁、叠瓦状断夹块、S-C 组构、X-Z 平面上的 C'剪切带,可以用作剪切方向指标。在微观尺度上,几乎所有的剪切带均发育不同类型的剪切运动指示构造,许多不对称结构,如 σ 型或 δ型碎斑、云母鱼、S-C 组构、 C'剪切带和 XZ 平面上的小褶皱等。此外,EBSD 显示的一些剪切带的石英 c 轴组构也被用作辅助标志。
-
3 阿拉善右行剪切系统
-
阿拉善地区的韧性右行走滑双重系统由一系列近东西走向、北西—南东向或北东走向的右行剪切带组成。这些剪切带具有相同的运动学特征,形成时代基本相同。下面就简单介绍构成阿拉善走滑双重系统的主要剪切带及剪切带之间地区的变形特征,详细研究请参考我们以及前人发表的成果 (Zhang et al.,2022a及所引文献)。
-
3.1 阿拉善南缘剪切带
-
阿拉善南缘剪切带整体呈北西-南东走向,沿着阿拉善地块南缘的宽滩山、黑山、合黎山和龙首山出露,长约500 km,出露宽度0.15~20 km(杨振德等,1988; Zhang et al.,2021a)。卷入剪切带的主要岩石为前寒武纪云母石英片岩、黑云斜长片麻岩和大理岩,早古生代绿泥石石英片岩和变长石石英砂岩,以及晚古生代花岗岩。阿拉善南缘韧性剪切带内糜棱面理陡倾,石英拉伸线理和矿物集合体线理近水平发育(图2),野外露头和镜下运动学标志一致指示该剪切带为右行走滑。根据被剪切带错断的早古生代岩体估算水平剪切位移量 40~50 km。剪切带活动温度约 500℃,运动学涡度表明该剪切带可能经历了由早期以简单剪切为主至晚期以纯剪切为主的剪切形式的变化。与剪切带相关的岩体锆石 U-Pb 年龄(151~269 Ma)以及糜棱岩化云母石英片岩新生云母矿物的40Ar/39Ar坪年龄给出的变形/冷却年龄(253~240 Ma),共同限定剪切带活动于 269~240 Ma。
-
3.2 北大山—巴彦诺尔公剪切带
-
北大山韧性剪切带目前相关的研究还非常零星,我们对它知之甚少。对该剪切带的具体形成时代、运动学性质和发育规模缺少约束。北大山红柳沟地区是北大山韧性剪切带的一部分,呈近东西向展布,延伸长度超过10 km,宽度约1 km。剪切带内所见岩性主要为长英质糜棱岩和少量花岗质糜棱岩,野外露头可见明显糜棱面理和矿物拉伸线理 (图3a),长英质糜棱岩面理上发育大量白云母,近水平的石英拉伸线理表明该剪切带主要以走滑剪切为主,花岗质糜棱岩长石旋斑指示右行走滑(图3b),镜下石英韧性变形强烈,发育石英丝带(图4a) 以及大量的 S-C 组构(图4a,b),共同指示右行剪切。
-
北大山韧性剪切带向东多被沙漠所覆盖,在一些局部露头上(如民勤以北),晚古生代花岗岩显示糜棱岩化(图5),但是剪切带的产状发生了改变,面理走向逐渐偏向北东,矿物线理的倾伏角逐渐变大,闪长质包体也被拉长定向(图3c),镜下长石碎斑发生旋转,构成对称构造以及 S-C 组构(图4c, d),共同指示了右行剪切。根据阿拉善地区的航磁异常推测,该剪切带延伸到巴彦诺尔公以东地区,在该地区前人已经报道发育剪切带(图5,Feng et al.,2020),但是对该剪切带的运动学性质和年代学目前还没有具体的约束。该地区韧性剪切带走向北北东(图5a),宽 5 km,长 17 km,卷入变形的主要是晚古生代的中—粗粒花岗岩,花岗岩的侵位年龄为 289 Ma(Feng et al.,2020)。值得注意的是该地区的韧性变形并不是走滑为主,而是斜冲为主 (图5c),石英拉伸线理陡倾(图2,5a)。在平行 XZ 面的薄片上显示右行运动(图5d,e)。
-
年代学方面前人已经开展了相关研究,对剪切带内发生糜棱岩中黑云母开展的40Ar/39Ar测年进一步限定北大山韧性剪切带形成时代为 274~264 Ma (Zhang et al.,2022a)。此外,根据宫江华等(2018) 对碾盘沟韧性变形所做的研究,糜棱岩化花岗岩的锆石 U-Pb 年龄(324~327 Ma),推测该剪切带可能形成于晚石炭世之后,与中亚造山带南缘晚古生代构造演化有关。而对巴彦诺尔公段的测年工作还比较薄弱,Feng et al.(2020)报道了卷入剪切带的花岗岩的原岩年龄(289 Ma),并推测该剪切带的活动时代为侏罗纪。
-
3.3 狼山—那仁哈拉—塔木素剪切带
-
狼山—那仁哈拉—塔木素剪切带是阿拉善地区一条规模较大的连续性好的剪切带,走向近东西走向,在航磁异常上也很明显,该构造带与查干础鲁蛇绿混杂岩带展布方向平行。自西向东,剪切带出露的长度超过 280 km,宽度在走向上变化较大,主要原因是第四纪沙漠的覆盖,出露不全,一般厚度在 500~4000 m。剪切带的主体发育在晚二叠世的花岗岩中(272~263 Ma, Zhang et al.,2022a,b),长英质糜棱岩发育,部分地区发育超糜棱岩,面理陡倾,矿物拉伸线理近于水平(图2,3f)。狼山等地区剪切带的具体几何学与运动学前人已经做了详细的报道,为近东西向陡倾的右行韧性剪切(Zhang et al.,2022a,b),而塔木素地区花岗糜棱岩镜下石英长轴斜列,与剪切面理构成S-C组构,指示也指示了右行剪切(图4e)。该剪切带在阿拉善地区东北端被三叠纪狼山—巴彦乌拉山左行韧性剪切带剪切(Zhang et al.,2013,2022b),结合前人研究确定狼山—那仁哈拉—塔木素剪切带活动时代为 250 Ma。
-
3.4 雅布赖剪切带
-
雅布赖山内部发育一条北东东走向韧性剪切带,该剪切带从西侧巴丹吉林沙漠东缘出露,走向大致75°方向延伸逾60 km,分隔南侧的雅布赖南山和北侧的雅布赖北山。该剪切带向东断续延伸到巴彦诺尔公以东地区,全长超过 200 km。该剪切带地貌上线性构造明显。剪切带宽度200~1000 m,围岩主要为早二叠世花岗闪长岩和前寒武纪变沉积岩。剪切带内的糜棱岩面理、矿物拉伸线理发育,线理产状近水平,表明主剪切带以走滑性质为主,兼有逆冲分量。剪切带面理产状近直立,不同段落因岩性不同糜棱岩类型不同,剪切带西段发育在中细粒花岗闪长岩岩体内,面理近直立,线理以石英拉伸线理为特征,局部见暗色包体拉伸线理,线理朝 SWW 方向倾伏,倾伏角小于 10°。剪切带中段围岩为含钾长石残斑的眼球状糜棱岩,面理发育而线理不发育。面理以黑云母定向排列为特征,在 XZ 面上发育S-C组构指示右行剪切。剪切带东段围岩为前寒武纪变沉积岩。剪切带内白云母39Ar/40Ar给出冷却年龄在254~252 Ma,表明该剪切带在晚古生代晚期存在活动。该剪切带详细的特征见 Zhao et al.(2022)。
-
图3 阿拉善晚古生代—早中生代主要右行韧性剪切带糜棱岩
-
a—北大山红柳沟云母石英糜棱岩及石英拉伸线理;b—北大山红柳沟花岗质糜棱岩“σ”型旋斑(右行剪切);c—民勤西北晚古生代花岗糜棱岩及剪切变形的闪长质包体和石英拉伸线理;d—塔木素晚古生代花岗糜棱岩及矿物拉伸线理;e—额济纳剪切带长英质糜棱岩及石英拉伸线理;f—那仁哈拉长英质糜棱岩及石英拉伸线理;g—雅布赖东侧晚古生代花岗糜棱岩;h—雅布赖东侧晚古生代花岗糜棱岩X-Z面长石旋斑 (右行走滑)
-
图4 阿拉善晚古生代—早中生代主要右行韧性剪切带显微照片(XZ面)
-
a—北大山剪切带石英丝带与S-C组构;b—北大山剪切带S-C组构;c—北大山剪切带S-C组构(民勤北);d—北大山剪切带钾长石碎斑(民勤北);e—塔木素剪切带S-C组构;f—额济纳剪切带S-C组构
-
3.5 额济纳剪切带
-
位于内蒙古额济纳旗东侧至雅干地区,靠近中蒙边界。剪切带内具丝绢光泽的云母片岩、二云片岩、石英云母片岩等构造片岩十分发育。构造片岩呈带状沿北东向延伸,主要在负地形的沟谷中出露,片理极为发育,构造片岩带边缘过渡为糜棱岩,糜棱面理与构造片岩产状基本一致,走向北东 40° 左右,倾向南东,倾角在50°~80°,野外发现的3条构造片岩带宽度在 200~300 m,长度 5~7 km。片理上的拉伸线理与片理走向一致,倾伏角近水平。根据剪切带切割的二叠系褶皱以及在二叠系中平行分布的一系列北北东走向小型左行断层(大型书斜构造),判断额济纳剪切带为右行剪切;而镜下,也见到很多 S-C 组构(图4f),这些都共同说明该剪切带是右行走滑。该剪切带的活动时代,前人曾测得糜棱岩化流纹斑岩锆石 U-Pb 年龄为 286 Ma,早二叠世闪长岩侵入体侵入绿条山组灰岩,年龄为 284~283 Ma,因此认为该剪切带形成时间应该为 286~284 Ma(早二叠世)(崔骁等,2019)。而最近的研究对采自该剪切带的白云母开展了40Ar/39Ar的年代学测试,其坪年龄为 253~237 Ma,但是该年龄被解释为受后期岩浆活动影响所致(王文宝等,2022)。
-
图5 巴彦诺尔公剪切带
-
a—巴彦诺尔公韧性剪切带地质图;b—晚古生代粗粒似斑状花岗糜棱岩剪切带野外特征; c—XZ面上的不对称长石旋斑,指示逆冲(镜像北北东);d—指示右行剪切带的钾长石碎斑;e—指示右行剪切带的斜长石碎斑
-
此外,还有银根剪切带、乌力吉和塔木素剪切带(图2),由于这 3条剪切带多数被覆盖,仅有零星出露,对其研究目前非常薄弱,尤其是银根剪切带,从中蒙边界向南西穿过巴丹吉林沙漠,主要走向是根据航磁异常推断,而其向东北则有可能与蒙古境内的Zunnbayan剪切带相连,而Zunnbayan断裂的韧性变形则是左行走滑(Lamb et al.,1999; Webb et al.,2010),与推测的银根右行剪切带矛盾,目前由于缺少资料,我们还不清楚该剪切带的具体信息,需要将来更多的工作。塔木素剪切带则位于宗乃山西侧,走向北北东,向东经过宗乃山转变为近东西走向,并一直延伸到中蒙边界(图2),在西侧该剪切带出露长度约 9 km,宽 150~2500 m,主体倾向南东,倾角 60°~80°,石英拉伸线理近水平。一系列不对称组构均显示该剪切带为右行韧性剪切(吴凤萍,2009),该剪切带向东研究程度很低,缺少必要的资料,其延伸主要依据航磁异常判定。乌力吉剪切带近东西走向,乌力吉以北晚古生代花岗岩局部表现出韧性变形,但具体研究很少,我们目前对其性质、时代以及规模都缺少认识,需要更多的研究。
-
3.6 弱变形域
-
阿拉善地区剪切带围限的地区一般韧性变形微弱,它们主要包括大型的侵入岩岩基(如宗乃山、沙拉扎山),这些侵入岩岩基一般都是晚古生代的花岗岩,除了在边缘出现了韧性变形,岩基内部没有发生韧性变形,部分岩基内部发育后期的岩墙群,其中一部分岩墙群的形成与边缘的韧性剪切活动有关。除了这些大型的花岗岩岩基外,弱变形域主要为中生代盆地占据的地区,这些盆地多为侏罗纪—白垩纪盆地,沉积厚度不一。油田钻井钻遇的基底岩石多为晚古生代沉积岩、火山岩和花岗岩,虽有变形,但是很少有韧性变形的报道(徐旺, 1999;魏仙样等,2014;吴晓智等,2015;卢进才等, 2018)。而一些中生代盆地的边界恰好与晚古生代韧性剪切带重合,例如雅布赖盆地。这些盆地都近东西向或北东向延伸,暗示早期基底构造对后期盆地的重要控制作用。
-
4 讨论
-
4.1 主要剪切带位移与时代
-
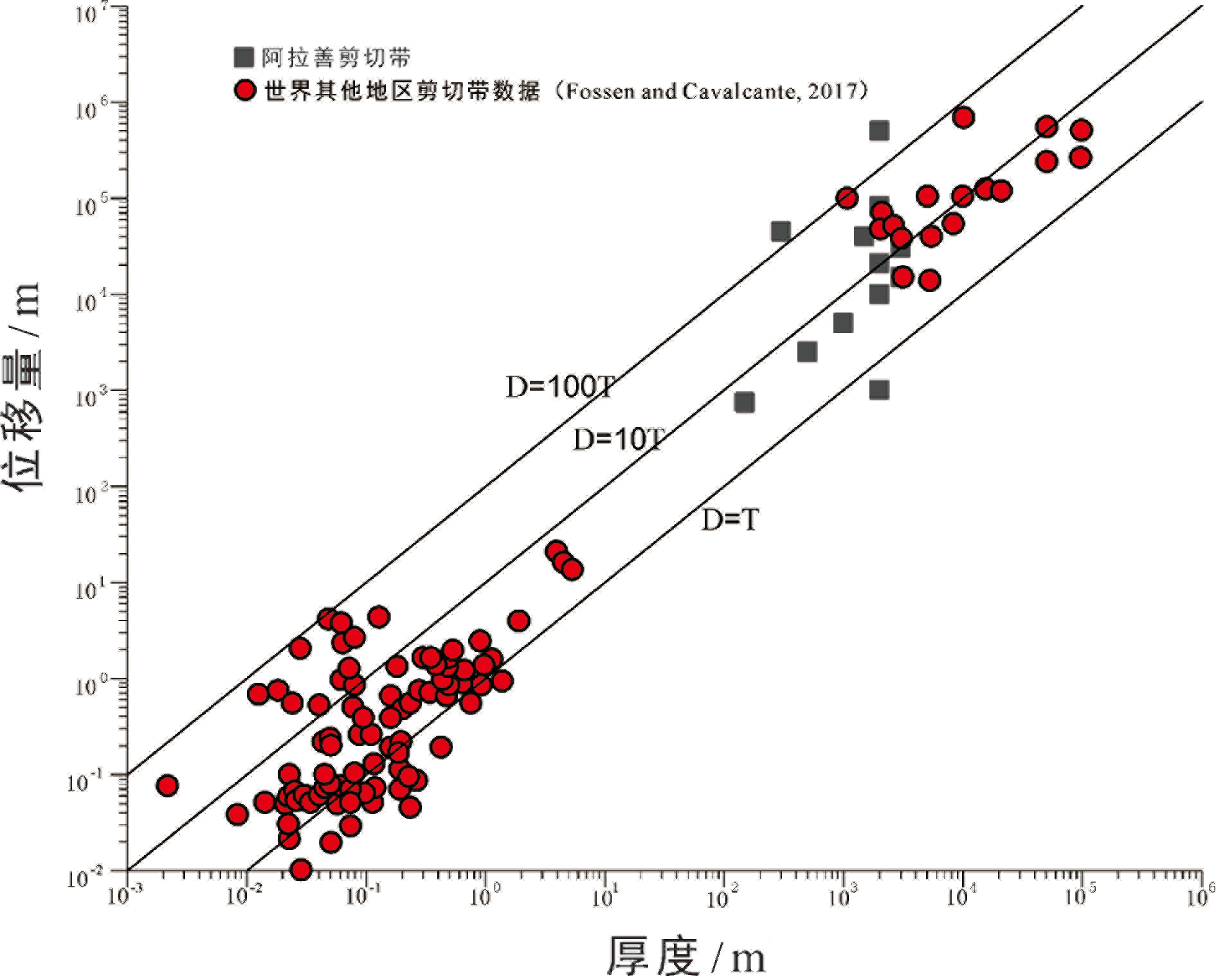
有关阿拉善晚古生代—早中生代剪切带位移量的计算,目前仅有龙首山剪切带和雅布赖剪切带有确定的野外约束,其中龙首山剪切带的位移量根据切割的古生代岩体计算可以达到40~50 km;雅布赖—巴彦诺尔公剪切带的位移量可以达到 21~30 km;而狼山—那仁哈拉—塔木素剪切带的位移量可达45~82 km(Zhang et al.,2022b)(表1)。位于阿拉善地块东缘的狼山—巴彦乌拉山剪切带规模最大,可以达到 180~200 km,然而该剪切带发生较晚(210 Ma)(Zhang et al.,2013a)。额济纳剪切带是最新发现的剪切带,其基本特征正在研究中,根据拖拽变形的二叠系褶皱,初步计算其走滑距离在10~17 km 之间(笔者未发表资料)。除此之外,阿拉善地区的同时代发育的右行韧性剪切带的走滑距离没有得到很好的限定。一般而言,剪切带中糜棱岩的形成,其剪切应变至少为 5(Ramsay and Graham, 1970; Simpson,1983),也有学者认为可以达到 10 (Fossen and Rykkelid,1990)。如果以剪切应变5为下限,根据出露的各个剪切带的宽度,可以大致得到不同剪切带的走滑位移量(表1)。从表中可以看出北大山—巴彦诺尔公剪切带的位移量为 2.5~25 km,而其长度却达到了 450 km,规模较大。与其规模类似的狼山—那仁哈拉—塔木素剪切带和龙首山剪切带的位移则达到了数十千米(表1),因此根据剪切应变 5 计算出的位移量很可能偏小。此外,由于沙漠的覆盖,目前还有两条可能的剪切带未得到有效控制,即银根剪切带和乌力吉剪切带(图2),这两条剪切带的规模与狼山—那仁哈拉—塔木素剪切带类似(图2),因此可能具有相近的走滑位移,可能达到了 40~80 km。我们把阿拉善地区有确定位移量的剪切带(表1)投到剪切带厚度-位移量图上,它们基本上都位于根据世界上韧性剪切带统计的范围内,说明剪切带位移量的判断是合理的(图6)。如果以剪切应变为 5 计算,这些剪切带累积位移量 240~430 km,而如果剪切应变为 10,累计位移量可以达到250~500 km。
-
随着近几年的工作,我们对阿拉善地区的韧性剪切带的定年取得了重要进展,除了乌力吉、银根以及塔木素剪切带没有很好的控制外,目前对多数出露良好的剪切带都已经有了同位素年代学的限定,这些剪切带多数活动发生在270~250 Ma(表1)。而乌力吉、银根以及塔木素剪切带由于切割了二叠纪的侵入岩,因此它们的活动时代很可能与其他剪切带同时。针对额济纳剪切带和北大山—巴彦诺尔公剪切带,崔骁等(2019)根据侵入到额济纳剪切带侵入岩的锆石年龄,约束该剪切带的变形年龄为 286~284 Ma;王文宝等(2022)对该剪切带也开展了年龄测试,白云母坪年龄为 253~237 Ma,但是认为该年龄是受到后期岩浆作用影响所致,根据同构造岩体限定的其走滑年龄为 331~288 Ma。上述白云母受后期岩浆作用影响的程度和具体机制目前不清楚,由于该剪切带明显切割了上二叠统,我们倾向认为该剪切带的时代比较晚,也在 270~250 Ma。 Feng et al.(2020)根据卷入到北大山—巴彦诺尔公剪切带的花岗岩锆石年龄推测剪切带在早侏罗世活动,但一直没有更确定的年龄。
-
图6 阿拉善晚古生代—早中生代主要剪切带位移量与厚度关系
-
注:* 根据剪切应变采用γ=5作为下限计算(Ramsay and Graham,1970; Simpson,1983; Fossen and Cavalcante,2017)。
-
4.2 走滑双重剪切系统
-
上述的几条剪切带都是目前在阿拉善地区识别出的晚古生代—早中生代的右行韧性剪切带。它们不仅时代相同,运动学性质也一致,但是它们分布没有明显的规律性,之间的关系也由于大面积的沙漠覆盖而不清楚。它们是否可以连接,还是遭受后期改造?以及是否还有更多的相同性质的剪切带没有被发现?深部数据有助于我们获得更多关于这些剪切带的信息,其中航磁异常数据是在覆盖区开展基底构造研究的重要的参考(Kane and Godson,1989; Sims et al.,2005; Fossen et al., 2022)。在巴西东部地区 Fossen 等就利用高精度的航磁资料限定了泛非造山期间形成的大型走滑双重构造组成及其走滑应变(Fossen et al.,2022)。
-
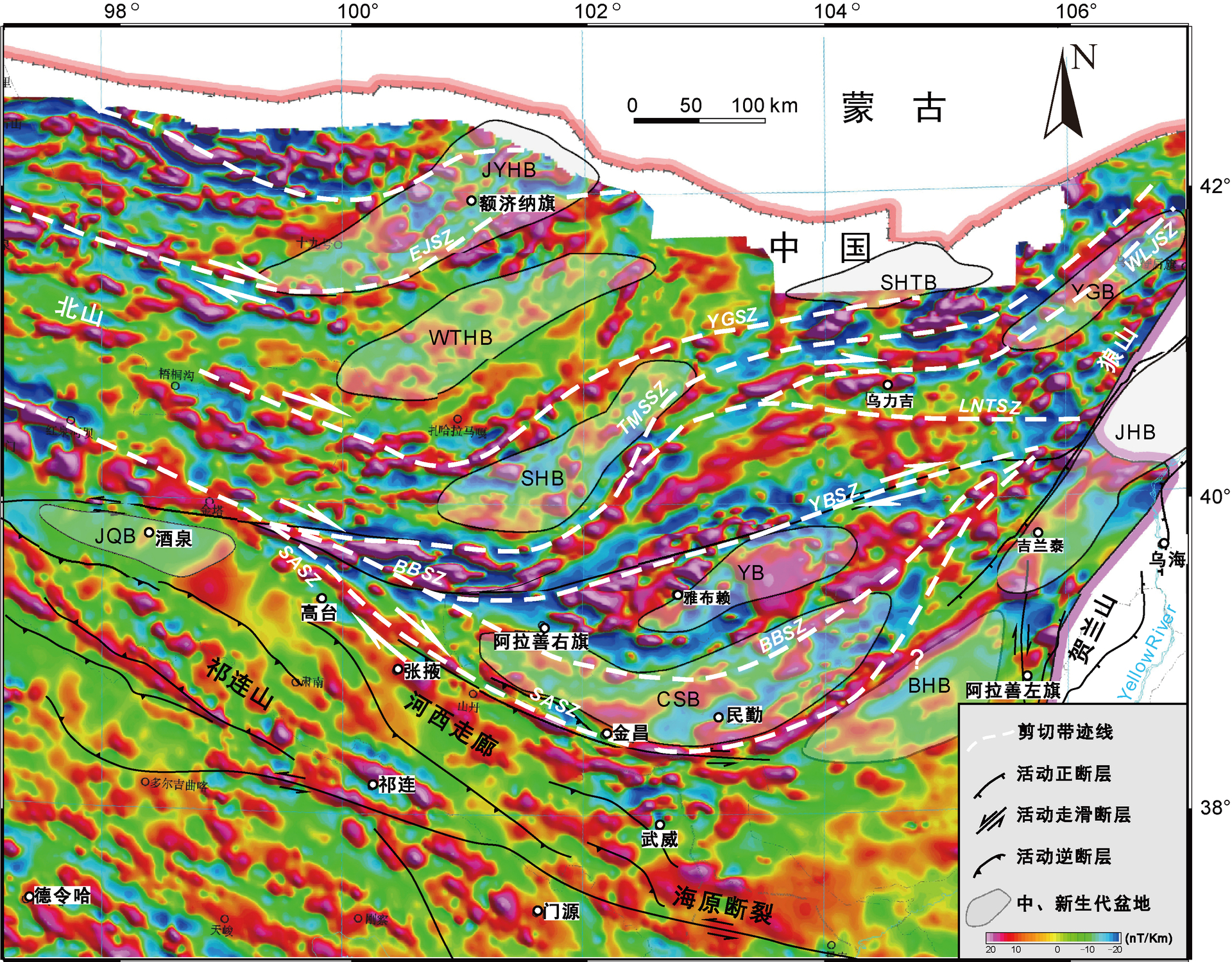
阿拉善地区的航磁异常非常独特,表现出一系列相间排列的弧形航磁异常(图7),而这些弧形异常带中的多数边界与地表出露的韧性剪切带很好地吻合。前人的研究表明在阿拉善地区的中北部磁场主要表现为东西向和北东东向宽缓升高变化的正磁场区,强度在10~100 nT之间。分析表明,阿拉善的剪切带主要与正航磁异常有关,这些正的异常主要是古生代的中、酸性侵入岩体(图7)(丁燕云和李占奎,1999;李玉宏等,2010)在异常中峰值较大,梯度较陡者一般为晚古生代中酸性侵入岩,而中生代基性火山岩及相应的侵入岩磁性最强,主要分布在东北部地区(图7),此外北大山—毛条山一带的深变质岩系具较强的磁性,而沉积岩的磁性一般较弱(丁燕云和李占奎,1999;李玉宏等,2010)。同时航磁异常图也显示了可能还有更多的地表未出露的韧性剪切带的存在,如上文提到的银根剪切带和乌力吉剪切带,而航磁异常也显示塔木素剪切带向东甚至可以延伸到中蒙边境地区(图7)。而本文提到的额济纳剪切带则是根据航磁异常的提示最近确定,虽然该剪切带最近也有研究成果发表 (崔骁等,2019),但是通过航磁异常进一步控制了该剪切带的空间延伸。
-
图7 阿拉善地区航磁异常及其解释(航磁异常底图据Xiong et al.,2016)
-
航磁异常图显示,阿拉善地区的这些晚古生代 —早中生代韧性剪切带组成一个平面上大型的 S-C like 的构造(图7)。这些剪切带向北东逐渐收敛合并到狼山—那仁哈拉—塔木素剪切带上,并被晚三叠世狼山—巴彦乌拉山左行韧性剪切带切割;向西南,阿拉善中南部的剪切带逐渐收敛合并到阿拉善南缘剪切带上,并可能与北山南部的剪切带相连,而阿拉善中部的银根剪切带以及北部的额济纳剪切带则向西延伸进入北山,分别与北山中部和北部的剪切带相连(Zhang et al.,2021a,2022a; Zhao et al.,2022)。而这个大型的 S-C like 的构造—同样也指示了右行剪切的运动学性质(图9)。变形分析表明,阿拉善地区的这些晚古生代—早中生代的韧性剪切带内部并没有经历强烈的后期变形改造,而且后期构造也主要利用了前期的构造,前期构造的总体格局并没有发生明显的改变;而改造的部分多集中在阿拉善的东部,该地区中、新生代经历了非常复杂的多阶段变形(Zhang et al.,2013a, 2014,2020,2022b; Zhao et al.,2020)。因此,目前阿拉善地区的航磁异常显示的深部结构体现了该地区晚古生代—早中生代的构造结构,刻画了该时段韧性剪切带的分布以及由它们组成的一个大型的韧性剪切系统,该系统平面上表现为一个大型的 S-C like 的构造,而该构造也是走滑双重构造的典型结构(Woodcock and Fisher,1986)。
-
为了进一步验证该剪切系统的存在,除了根据地表地质填图确定一些未知的韧性剪切带外,笔者也对剪切带围限的岩墙群开展了定年和分析。岩墙群发育在造山带变形的研究中具有重要的作用,因为它能指示最小主压应力方向(Dewey,2002; Şengör et al.,2019)。在阿拉善和北山地区发育了大量的晚古生代和早中生代的岩墙群(Zhang et al.,2022a及所引文献),这些岩墙群的发育时代与阿拉善地区的韧性剪切变形发育同时,两者之间可能存在关联。笔者对阿拉善地区发育的岩墙进行了分析(图8),可以发现该地区存在多期岩墙群的发育,如图克木以及红沙岗地区,这些岩墙主要为中基性的辉绿岩岩脉和酸性的花岗斑岩岩脉,但最发育的是晚期的北西—南东走向的岩墙群(图8),部分为近南北向(如红沙岗,图10),而早期的岩墙群走向多变,北西、北东、南北走向均有发育(图8)。笔者以及前人对这些岩墙群开展了年代学测试,其中北西—南东走向的岩墙群年龄为240~263 Ma(图8),而其他的方向的则较老,如红沙岗地区近东西向的辉绿岩为319 Ma(图8,Zhang et al.,2022a)。
-
阿拉善地区的这些北西—南东向和近南北向岩墙群分布有一定的规律,它们都几乎分布在晚古生代—早中生代韧性剪切带的附近(图8),而这些近东西向的右行剪切带在活动时,会形成北西—南东向的局部主压应力场,导致形成一系列与剪切带呈大角度(~45°)伸展构造,类似的现象在走滑断层系统中非常常见(Sylvester,1988),因此我们将阿拉善地区晚古生代—早中生代北西—南东向岩墙群的形成归结于同时代的右行韧性剪切作用,而近南北向的同时代的岩墙群(红沙岗)的形成与北西走向的北大山—巴彦诺尔公剪切带有关(图8)。类似的现象在北山地区也广泛分布,说明阿拉善地区的这些韧性剪切带向西可与北山地区的韧性剪切带相连(Zhang et al.,2022a)。
-
4.3 走滑双重构造形成的温度压力
-
随着研究的积累,阿拉善晚古生代—早中生代韧性剪切带形成时的温度和压力有了一定的研究,目前确定韧性剪切变形的温度主要通过EBSD石英组构测试,并结合传统的镜下变形矿物(石英)特征的判断。目前已有的结果均显示,阿拉善地区主要的晚古生代—早中生代右行韧性变形的温度为 300~500℃(表2),变形环境为绿片岩相,如果按照 25~30℃/km 的地温梯度计算,变形的深度为 10~12 km。而这个温度条件下,位于云母类矿物的封闭温度区间(黑云母:250~350℃;白云母:350~450℃),锆石的封闭温度是900℃。虽然目前有数据约束的剪切带有5条(表2),但这5条基本上都是规模较大的剪切带,而且分布在几乎整个阿拉善地区,因此可以推测发生变形的时候,整个阿拉善整体不仅参与了变形,而且当时变形的深度也差不多,说明当时的阿拉善地壳厚度和地温梯度基本保持一致。
-
此外,本文介绍的右行韧性变形多发育在晚古生代的中、酸性侵入岩中,这些岩体的侵位时代一般在 280~250 Ma(表2),而多数变形年龄在 260~250 Ma。从锆石封闭温度(900℃)到云母类矿物的封闭温度(250~450℃)冷却时间一般为 20 Ma(表2)。通过这些数据可以计算当时主要剪切带的冷却速率,几条约束较好的剪切带计算出的冷却速率平均为 30℃/Ma(表2),这代表了快速的冷却 (Thiede and Ehlers,2013;Neves et al.,2021),而少数年代学限定不好的剪切带(如北大山—巴彦诺尔公剪切带),冷却速率约为 10℃/Ma左右(表2)。目前其他几条剪切带还缺少必要的数据,还需要更多的工作限定。
-
同时,从阿拉善地区侵入岩分布图上也可以看出,整个阿拉善地区侵入岩分布广泛,并相对均匀 (图9)。这些侵入岩中除了少数是早古生代或者新元古代外,绝大多数是晚古生代的中、酸性侵入岩 (图2及其文献)。这些岩浆岩的侵入导致了阿拉善地区晚古生代热结构以及物质组成的变化,而这些变化直接导致了阿拉善地壳流变学性质发生改变。已有的研究也表明,侵入热地壳的侵入岩一般能够保持其温度较围岩高长达几个到几十个百万年 (Davidson et al.,1992; Tommasi et al.,1994),而在随后的变形中,变形往往集中在侵入体的边缘,类似的现象在其他的韧性走滑双重系统中也有发现 (Neves and Mariano,1999;Neves et al.,2021)。
-
图8 阿拉善地区岩墙群分布
-
A—右行韧性剪切带与岩墙群的空间分布关系;B—红沙岗(民勤北)两组方向不同岩性岩墙群及锆石年龄;C—红沙岗岩墙群;D—图克木不同方向岩墙群及锆石年龄;E—巴彦诺尔公岩墙群及锆石年龄
-
图9 阿拉善地区侵入岩分布及与走滑双重构造的关系
-
(推断的侵入岩分布据熊盛青等,2020)
-
4.4 阿拉善走滑双重构造的形成背景与机制
-
阿拉善地区的晚古生代—早中生代走滑双重构造系统的形成并不孤立,在同时代,沿着整个中亚造山带的南缘普遍发育了一期强烈的韧性右行走滑事件,这个近东西向的韧性剪切系统可能是横切潘基亚超大陆中部的大型剪切系统的组成部分 (Zhang et al.,2022a)。由于在阿拉善及其以东地区观察到了该剪切系统切割早期古亚洲洋碰撞导致形成的构造(Zhang et al.,2022a,b),因此笔者认为这期沿着中亚造山带南缘的大型右行韧性剪切发生在古亚洲洋关闭之后,是中亚造山带发育的第一期陆内变形。导致该右行剪切的机制目前还不很清楚(Zhang et al.,2022a),但是在晚古生代末期西伯利亚与波罗的克拉通的相向旋转靠近已经为古地磁研究所证实(Van der Voo et al.,2006),这个过程造成了位于两个克拉通之间的中亚造山带整体发生变形,并向东挤出,随着物质的向东移动,在造山带的南缘随即形成了一系列的右行韧性剪切。
-
阿拉善位于中亚造山带中段,在古亚洲洋演化的过程中形成了一系列的边缘弧和增生楔。同时,伴随着强烈的岩浆作用,形成了遍及整个阿拉善的侵入岩体。虽然目前对阿拉善的属性有不同认识,但是强烈的岩浆作用以及岛弧/地块的拼贴增生,导致了阿拉善原有的地壳结构发生了强烈变化,这为后续的变形奠定了基础。阿拉善与华北克拉通的关系虽然有非常多的认识,但随着古亚洲洋的关闭,阿拉善与华北克拉通的相对位置就已经基本固定,虽然在晚三叠世,阿拉善与华北克拉通之间沿着狼山—巴彦乌拉山剪切带曾经发生过 180~200 km的左行位移(Zhang et al.,2013a),但是基本没有改变阿拉善与华北的相对位置关系。将晚三叠世的变形恢复后,阿拉善仍然位于华北克拉通的西北部(图10)。
-
随着晚古生代末期中亚造山带物质整体的向东挤出,阿拉善地区经历右行剪切,由于广泛的岩浆作用和岛弧/地块拼贴增生造山,强烈改造了该地区地壳的流变学性质,主要的剪切作用集中于重要组成单元的边界(如大型花岗岩岩基)。在阿拉善一些大型的花岗岩岩基以及主要岛弧/地块主要呈近东西向展布,因此它们就控制了阿拉善走滑系统的主要结构。然而继续向东,中亚造山带部分物质在向东的运动则受到了东侧华北克拉通西北部的阻挡,导致了该地区应力的集中,该地区也位于右行走滑的缩短应变象限中,最终导致了在阿拉善地区形成了 S-C like 的大型韧性右行走滑双重构造 (图10)。笔者将阿拉善走滑双重系统的形成归结于增生造山改造的地壳结构、华北克拉通的位置以及大范围的造山带物质东移共同造成的结果 (图10)。
-
图10 中亚造山带阿拉善走滑双重系统及其东西两侧剪切带连接模型
-
4.5 大型走滑双重构造的作用与区域构造意义
-
近20年来,阿拉善地块的属性一直是一个有争议的问题,可以分为 3 种重要认识:(1)古元古代或更早就已经成为华北克拉通的一部分(Huang, 1945; Zhao et al.,2005);(2)一个独立的块体,在古生代早中期成为华北板块的一部分(Zhang et al.,2013a,2015a,2022b; Dan et al.,2014);(3)中亚造山带中的一个构造带(Song et al.,2018)。阿拉善大型剪切系统的分布和发育显示很难将其作为一个克拉通或者板块的一部分对待,尤其是比较均匀分布的古生代花岗岩更进一步说明了其基底并非一个整体,而是被众多剪切带分隔的构造堆叠体,这个堆叠体中既包括了岛弧、增生楔,也可能包括了早期的地块或被肢解的地块。如果从这个角度出发,我们目前看到的阿拉善则更类似一个构造带(图10),但是这并不排除其早期具有地块属性的可能性。
-
阿拉善的这个大型走滑双重构造南北宽约350 km,东西长约500 km,而向北可能进入南蒙古地区。如此规模的走滑双重构造在中亚造山带的研究中还很少报道。在中亚造山带内是否还存在类似阿拉善走滑双重构造的构造目前还不得而知,而阿拉善的双重构造的发育除了受控于特殊的条件外,可能代表了不同的变形环境和条件。它的发育也是东西两侧不同构造的过渡地区(图10)。阿拉善西侧的天山地区也发育有几条不同方向的右行韧性剪切带,但是这些剪切带处于南侧塔里木克拉通、伊犁地块以及准噶尔地块之间,它们受控于这些构造单元,分布在面积广大的地区,走滑作用往往集中在这些剪切带上,其宽度和位移量往往也较阿拉善地区的剪切带高一个量级以上(Zhang et al., 2022a)。相对于天山地区的韧性走滑,阿拉善地区的右行韧性剪切带显得更具“透入性”。阿拉善东侧,已有的研究在华北克拉通北缘和兴蒙造山带发现了同时代的韧性剪切,但是剪切带的数量明显变少,规模也相应变小,主要的剪切带基本沿着华北克拉通北缘分布(Wang and Wan,2014; Zhao et al.,2015; Zhang et al.,2022a),体现了克拉通对剪切带的重要控制作用。阿拉善东西两侧与阿拉善地区的韧性剪切最大的不同就是克拉通或者地块的尺度变大,地壳横向不均一性显著,它们在控制剪切带分布上具有更大的作用,而阿拉善地区地壳结构横向不均一性并不是很显著,因此造成的变形也相对均匀分布,这可能是不同地壳结构造成的不同的应变形式。需要指出的是阿拉善这些韧性剪切带成为影响或者控制晚期陆内变形的重要因素 (Zhang et al.,2020),例如,早白垩世伸展在阿拉善地区呈面状分布,而控制这些断陷盆地的往往就是早期的韧性剪切带再次活动而导致(图7)。
-
阿拉善的韧性走滑双重系统从规模上与印度南部(Chardon et al.,2008)以及巴西东部 Borborena 韧性走滑双重系统(Corsini et al.,1996; Neves and Mariano,1999; Neves et al.,2021; Fossen et al., 2022)类似。特别是与巴西东部的Borborena韧性走滑双重系统有很多类似之处。首先,这两个剪切系统规模都类似,都具有约200000 km2 的面积,位移量也在 200~500 km(Neves et al.,2021; Fossen et al., 2022);第二,两者都发育于增生型造山带内,阿拉善韧性双重系统发育在显生宙最大的增生型造山带—中亚造山带内部,而Borborena韧性双重系统则发育在新元古代的泛非造山带中(Neves et al., 2021; Fossen et al.,2022),而增生型造山中广泛的岩浆作用为后续剪切带的分布和形成提供了物质和结构基础,阿拉善双重系统和Borborena韧性走滑双重系统均包含了大量的侵入岩,而伴随造山作用的岩浆作用会影响地壳的横向上热结构的变化以及强度的变化,很多大型的剪切带常沿着大型花岗岩岩基的边缘发育,而围岩则很少受到剪切作用的影响(Neves and Mariano,1999;Neves et al.,2021); 第三,两者都发育在主造山事件之后 10~20 Ma 内,中亚造山带中段阿拉善地区古亚洲洋关闭的时限虽然有不同认识(Shi et al.,2016;Song et al., 2018,2020;Zhang et al.,2021b),但主要观点认为大洋关闭的时间为约晚二叠世之前(280~265 Ma) (Shi et al.,2014;Zheng et al.,2014;Liu et al., 2017a,b,2019a,b; Hui et al.,2021; Zhang et al., 2022a,b),阿拉善韧性双重系统形成时间约 260~250 Ma;而Borborena韧性双重系统则是发育在泛非造山作用主造山阶段之后约 20 Ma(Neves et al., 2021);第四,古老克拉通都起到了重要作用,阿拉善走滑双重构造的形成与中亚造山带向东的构造挤出,遇到华北克拉通的阻挡,导致在华北克拉通西北角产生应变集中,形成了走滑双重构造;而 Borborena 韧性走滑双重系统同样也是造山带物质向东运动并受到了 São Francisco 克拉通的阻挡,在该克拉通的西北角造成应变集中而形成(Corsini et al.,1996; Neves et al.,2021)。第五,阿拉善与 Borborena韧性双重系统都具有相同的冷却速率,都约为 30℃/Myr,可能代表了与韧性走滑剪切伴随的重要剥露过程。
-
5 结论
-
大型走滑双重构造是造山带中重要的变形方式,它受控于地壳的热结构以及不均一的物质组成和边界条件,与地壳的流变学性质息息相关。阿拉善晚古生代—早中生代大型右行韧性走滑双重构造发育于中亚造山带中段,其面积约200000 km2,由 7~8 条次级的右行韧性剪切带组成,主要剪切带分布在大型花岗岩岩基的边缘。单条剪切带的走滑位移10~60 km,累积走滑距离可达300~500 km。阿拉善大型右行韧性走滑双重构造是中亚造山带南缘大型剪切系统的重要组成部分,是造山带物质向东运动受到华北克拉通的局部阻挡应变集中而形成,阿拉善整体都参与了变形,其属性更像造山带,而非克拉通。阿拉善韧性走滑双重系统是连接中亚造山带东西不同变形场的枢纽,代表了应变传递的一种方式。大型韧性走滑双重构造是增生型造山带常见构造之一,它们不仅可以造成构造单元的构造堆叠重复,同时它也是造山带后期陆内变形的重要控制因素之一。
-
致谢 本文是作者团队十余年来在中亚造山带工作的一点心得和发现,不当之处难免存在,一些想法也不够成熟,仅希望能够抛砖引玉。感谢审稿人提出的宝贵意见和编辑部的诚挚邀请撰写此稿。
-
参考文献
-
Chardon D, Jayananda M, Chetty T R K, Peucat J J. 2008. Precambrian continental strain and shear zone patterns: South Indian case[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 113(B08402): 1–16, doi: 10. 1029/2007JB005299
-
Corsini M, Vauchez A, Caby R. 1996. Ductile duplexing at a bend of a continental-scale strike-slip shear zone: Example from NE Brazil [J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 18(4): 385–394.
-
Cunningham D. 2013. Mountain building processes in intracontinental oblique deformation belts: Lessons from the Gobi Corridor, Central Asia[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 46(1): 255 –282.
-
Cunningham W D. 2007. Structural and topographic characteristics of restraining bend mountain ranges of the Altai, Gobi Altai and easternmost Tien Shan[J]. Geological Society Special Publications, 290(1): 219–238.
-
Dan W, Li X H, Wang Q, Tang G J, Liu Y. 2014. An Early Permian (ca. 280 Ma) silicic igneous province in the Alxa Block, NW China: A magmatic flare-up triggered by a mantle plume?[J]. Lithos, 204(9): 144–158.
-
Dan W, Li X H, Wang Q, Wang X C, Wyman D A, Liu Y. 2015a. Phanerozoic amalgamation of the Alxa Block and North China Craton: Evidence from Paleozoic granitoids, U-Pb geochronology and Sr–Nd–Pb–Hf–O isotope geochemistry[J]. Gondwana Research, 32(4): 105–121.
-
Dan W, Wang Q, Wang X C, Liu Y, Wyman D A, Liu Y S. 2015b. Overlapping Sr – Nd – Hf – O isotopic compositions in Permian mafic enclaves and host granitoids in Alxa Block, NW China: Evidence for crust – mantle interaction and implications for the generation of silicic igneous provinces[J]. Lithos, 230(8): 133 –145.
-
Dan W, Li X H, Wang Q, Wang X C, Wyman D A, Liu Y. 2016. Phanerozoic amalgamation of the Alxa Block and North China Craton: Evidence from Paleozoic granitoids, U-Pb geochronology and Sr–Nd–Pb–Hf–O isotope geochemistry[J]. Gondwana Research, 32(4): 105–121.
-
Davidson C, Hollister, L S, Schmid S M. 1992. Role of melt in the formation of a deep crustal compressive shear zone: The Maclaren Glacier metamorphic belt, south central Alaska[J]. Tectonics, 11 (4): 348–359.
-
Dewey J F. 2002. Transtension in Arcs and Orogens[J]. International Geology Review, 44(5): 402–439.
-
Feng Y P, Zhang W J, Wang G H, Li D, Lu Y. 2020. Plastic deformation and rheology of the sinistral strike‐slip ductile shear zone in the Bayan Nuru area, Alxa Zuoqi, NW China: Product of subduction of Paleo-Pacific Plate[J]. Geological Journal, 55(3): 1984 –1998.
-
Fossen H, Cavalcante G C G. 2017. Shear zones – A review[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 171(8): 434–455.
-
Fossen H, Harris L B, Cavalcante C, Archanjo C J, Ávila C F. 2022. The Patos-Pernambuco shear system of NE Brazil: Partitioned intracontinental transcurrent deformation revealed by enhanced aeromagnetic data [J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 158 (104573): 1-17.
-
Fossen H, Rykkelid E. 1990. Shear zone structures in the Øygarden area, western Norway[J]. Tectonophysics, 174(3/4): 385–397.
-
Hu C S, Li W B, Xu C, Zhong R C, Zhu F, Qiao X Y. 2015. Geochemistry and petrogenesis of Permian granitoids in the northwestern margin of the North China Craton: Insights from the Dongshengmiao pluton, Inner Mongolia[J]. International Geology Review, 57(14): 1843–1860.
-
Hui J, Zhang K J, Zhang J, Qu J F, Zhang B H, Zhao H, Niu P F. 2021. Middle–Late Permian high-K adakitic granitoids in the NE Alxa block, northern China: Orogenic record following the final closure of Paleo-Asian Ocean?[J]. Lithos, 400/401(1): 106379.
-
Huang T K. 1945. On the major tectonic forms of China[J]. Geological Memoir (Ser. A)20: 1–165.
-
Jahn B M. 2004. The Central Asian Orogenic Belt and growth of the continental crust in the Phanerozoic[J]. Geological Society Special Publication, 226(1): 73–100.
-
Kane M F, Godson R H. 1989. A crust/mantle structural framework of the conterminous United States based on gravity and magnetic trends[C]// Pakiser L C, Mooney W D. Geophysical Framework of the Continental United States: Boulder, Colorado, Geological Society of America Memoir 172: 383–403.
-
Kumar P S. 2005. An alternative kinematic interpretation of Thetis Boundary Shear Zone, Venus: Evidence for strikeslip ductile duplexes[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 110(E7): E07001.
-
Lamb M A, Hanson A D, Graham S A, Badarch G, Webb L E. 1999. Left-lateral sense offset of upper Proterozoic to Paleozoic features across the Gobi Onon, Tost, and Zuunbayan faults in southern Mongolia and implications for other Central Asian faults[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 173(3): 183–194.
-
Li R W, Zhang X, Shi Q, Chen W F, An Y, Huang Y S, Liu Y X, Wang J R. 2020. Early Permian to Late Triassic tectonics of the southern Central Asian Orogenic Belt: Geochronological and geochemical constraints from gabbros and granites in the northern Alxa area, NW China[J]. Geological Magazine, 157(12): 1 –17.
-
Lin L N, Xiao W J, Wan B, Windley B F, Ao S J, Han C M, Feng J Y, Zhang J E, Zhang Z Y. 2014. Geochronologic and geochemical evidence for persistence of south-dipping subduction to Late Permian time, Langshan Area, Inner Mongolia (China) : Significance for termination of accretionary orogenesis in the southern altaids[J]. American Journal of Science, 314(2): 679 –703.
-
Liu M, Zhang D, Xiong G Q, Zhao H T, Di Y J, Wang Z, Zhou Z G. 2016a. Zircon U-Pb age, Hf isotope and geochemistry of Carboniferous intrusions from the Langshan area, Inner Mongolia: Petrogenesis and tectonic implications[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 120(15): 139–158.
-
Liu Q, Zhao G C, Han Y G, Eizenhöfer P R, Zhu Y L, Hou W Z, Zhang X R. 2017a. Timing of the final closure of the Paleo-Asian Ocean in the Alxa terrane: Constraints from geochronology and geochemistry of Late Carboniferous to Permian gabbros and diorites [J]. Lithos, 274/275(3): 19–30.
-
Liu Q, Zhao G C, Han Y G, Eizenhöfer P R, Zhu Y L, Hou W Z, Zhang X R, Wang B. 2017b. Geochronology and geochemistry of Permian to Early Triassic granitoids in the Alxa Terrane: Constraints on the final closure of the Paleo-Asian Ocean[J]. Lithosphere, 9(4): 665–680.
-
Liu Q, Zhao G C, Han Y G, Li X P, Zhu Y L, Eizenhöfer P R, Zhang X R, Wang B, Tsui R W. 2018. Geochronology and Geochemistry of Paleozoic to Mesozoic Granitoids in Western Inner Mongolia, China: Implications for the Tectonic Evolution of the Southern Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. The Journal of Geology, 126(4): 451–471.
-
Liu Q, Zhao G C, Han Y G, Zhu Y L, Wang B, Eizenhöfer P R, Zhang X R, Tsui R W. 2019a. Timing of the final closure of the middle segment of the Paleo-Asian Ocean: Insights from geochronology and geochemistry of Carboniferous-Triassic volcanosedimentary successions in western Inner Mongolia, China [J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 131(5/6): 941 –965.
-
Liu Q, Zhao G C, Sun M, Han Y G, Eizenhofer P R, Hou W Z, Zhang X R, Zhu Y L, Wang B, Liu D X, Xu B. 2016b. Early Paleozoic subduction processes of the Paleo-Asian Ocean: Insights from geochronology and geochemistry of Paleozoic plutons in the Alxa Terrane[J]. Lithos, 262(10): 546–560.
-
Liu Z, Zhang X, Tan S C, Sha X, He X H, Zhou Q. 2019b. The timing of the Paleo-Asian Oceanic closure: Geochemical constraints from the Jigede gabbro in the Alxa Block[J]. Petrology, 27(4): 425–437.
-
Mann P. 2007. Global catalogue, classification and tectonic origins of restraining and releasing bends on active and ancient strike-slip fault systems[J]. Geological Society Special Publications, 290 (1): 13–142.
-
Marshak S, Nelson W J, McBride J H. 2003. Phanerozoic strike-slip faulting in the continental interior platform of the United States: Examples from the Laramide Orogen, Midcontinent, and ancestral Rocky Mountains[J]. Geological Society Special Publications, 210 (1): 159–184.
-
Neves S P, Mariano G. 1999. Assessing the tectonic significance of a large-scale transcurrent shear zone system: The Pernambuco lineament, northeastern Brazil[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 21 (10): 1369–1383.
-
Neves S P, Tommasi A, Vauchez A, Carrino T A. 2021. The Borborema strike-slip shear zone system (NE Brazil): Large-scale intracontinental strain localization in a heterogeneous plate [J]. Lithosphere, 2021(6): 6407232.
-
Niu P F, Qu J F, Zhang J, Zhang B H, Zhao H. 2022. Precambrian tectonic affinity of the Southern Langshan Area, northeastern margin of the Alxa Block: Evidence from zircon U‐Pb dating and Lu‐Hf isotopes[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica (English Edition), 96 (5): 1516–1533.
-
Ramsay J G, Graham R H. 1970. Strain variation in shear belts[J]. Canadian Jounral of Earth Sciences, 7(3): 786–813.
-
Sengör A M C, Natal’in B A. 1996. Paleotectonics of Asia: Fragments of a synthesis[C]//Yin A, Harrison T M (eds. ). The Tectonic Evolution of Asia. Cambridge University Press, New York. P: 486 –640.
-
Sengör A M C, Natal’in B A, Burtman V S. 1993. Evolution of the Altaid tectonic collage and Palaeozoic crustal growth in Eurasia [J]. Nature, 364(6435): 299–307.
-
Sengör A M C, Natal’in B A, Sunal G, van der V R. 2018. The tectonics of the Altaids: Crustal growth during the construction of the continental lithosphere of Central Asia between 750 and~ 130 Ma ago[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 46(1): 439–494.
-
Sengör A M C, Zabc C, Natal’in B A. 2019. Continental transform faults: Congruence and incongruence with normal plate kinematics [C]//Transform Plate Boundaries and Fracture Zones. Elsevier: 169–247.
-
Shi G Z, Song G Z, Wang H, Huang C Y, Zhang L D, Tang J R. 2016. Late Paleozoic tectonics of the Solonker Zone in the Wuliji area, Inner Mongolia, China: Insights from stratigraphic sequence, chronology, and sandstone geochemistry[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 127(13): 100–118.
-
Shi G Z, Wang H, Liu E T, Huang C Y, Zhao J X, Song G Z, Liang C. 2018. Sr–Nd–Pb isotope systematics of the Permian volcanic rocks in the northern margin of the Alxa block (the Shalazhashan Belt) and comparisons with the nearby regions: Implications for a Permian rift setting?[J]. Journal of Geodynamics, 115(4): 43 –56.
-
Shi X J, Wang T, Zhang L, Castro A, Xiao X C, Tong Y, Zhang J J, Guo L, Yang Q D. 2014. Timing, petrogenesis and tectonic setting of the Late Paleozoic gabbro–granodiorite–granite intrusions in the Shalazhashan of northern Alxa: Constraints on the southernmost boundary of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Lithos, 208/209(11): 158–177.
-
Simpson C. 1983. Displacement and strain patterns from naturally occurring shear zone terminations[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 5(5): 497–506.
-
Sims P K, Saltus R W, Anderson E D. 2005. Preliminary Precambrian Basement Structure Map of the Continental United States-An Interpretation of Geologic and Aeromagnetic Data[R]. Open-File Report 2005–1029, U. S. Geological Survey, 1–29.
-
Song D F, Xiao W J, Collins A S, Glorie S, Han C M, Li Y C. 2018. Final subduction processes of the Paleo-Asian Ocean in the Alxa Tectonic Belt (NW China): Constraints from field and chronological data of Permian arc-related volcanosedimentary rocks[J]. Tectonics, 37(6): 1658–1687.
-
Song D F, Xiao W J, Windley B F, Han C M. 2020. Carboniferous to Early Triassic magmatism and accretion in Alxa (NW China): Implications for accretionary orogenesis of the southern Altaids [J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 177(5): 997–1012.
-
Song D F, Xiao W J, Windley B F, Han C M. 2021. Provenance and tectonic setting of late Paleozoic sedimentary rocks from the Alxa Tectonic Belt: implications for accretionary tectonics of the southern Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 133(1/2): 253–275.
-
Storti F, Holdsworth R E, Salvini F. 2003. Intraplate strike-slip deformation belts[J]. Geological Society Special Publications, 210 (1): 1–14.
-
Sylvester A G. 1988. Strike-slip faults[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 100(11): 1666–1703.
-
Thiede R C, Ehlers T A. 2013. Large spatial and temporal variations in Himalayan denudation[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 371–372(6): 278–293.
-
Tommasi A, Vauchez A, Fernandes L A D, Porcher C C. 1994. Magma-assisted strain localization in an orogen–parallel transcurrent shear zone of southern Brazil[J]. Tectonics 13(2): 421 –437.
-
Van der Voo R, Levashov N M, Skrinnik L I, Kara T V, Bazhenov M L. 2006, Late orogenic, large-scale rotations in the Tien Shan and adjacent mobile belts in Kyrgyzstan and Kazakhstan[J]. Tectonophysics, 426(3): 335–360.
-
Wang Z Z, Han B F, Feng L X, Liu B. 2015. Geochronology, geochemistry and origins of the Paleozoic–Triassic plutons in the Langshan area, western Inner Mongolia, China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 97(B): 337–351.
-
Wang Z H, Wan J L. 2014. Collision-Induced Late Permian-Early Triassic transpressional deformation in the Yanshan Tectonic Belt, North China[J]. The Journal of Geology, 122(6): 705–716.
-
Webb L E, Johnson C L, Minjin C. 2010. Late Triassic sinistral shear in the east Gobi fault zone, Mongolia[J]. Tectonophysics, 495 (3): 246–255.
-
Woodcock N H, Fischer M. 1986. Strike-slip duplexes[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 8(7): 725–735.
-
Xiao W J, Windley B F, Huang B C, Han C M, Yuan C, Chen H L, Sun M, Sun S, Li J L. 2009. End-Permian to mid-Triassic termination of the accretionary processes of the southern Altaids: Implications for the geodynamic evolution, Phanerozoic continental growth, and metallogeny of Central Asia[J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 98(6): 1189–1217.
-
Xiao W J, Windley B F, Sun S, Li J L, Huang B C, Han C M, Yuan C, Sun M, Chen H L. 2015. A tale of amalgamation of three Permo-Triassic collage systems in Central Asia: Oroclines, sutures, and terminal accretion[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 43(1): 477–507.
-
Xiong S Q, Tong J, Ding Y Y, Li Z K. 2016. Aeromagnetic data and geological structure of continental China: A review[J]. Applied Geophysics, 13(2): 227–237.
-
Xue S, Ling M X, Liu Y L, Zhang H, Sun W D. 2017. The genesis of Early Carboniferous adakitic rocks at the southern margin of the Alxa Block, North China[J]. Lithos, 278/281(5): 181–194.
-
Yang H, Yang X, Cunningham D, Hu Z, Huang X, Huang W, Yang H, Miao S, Zhang L. 2020. A regionally evolving transpressional duplex along the northern margin of the Altyn Tagh Fault: New kinematic and timing constraints from the Sanweishan and Nanjieshan, China[J]. Tectonics, 39(e2019TC005749): 1–28.
-
Zhang B H, Zhang J, Zhao H, Zhang Y P, Qu J F, Niu P F, Wang Y N, Hui J. 2021a. Kinematics and geochronology of Late Paleozoic – Early Mesozoic ductile deformation in the Alxa Block, NW China: New constraints on the evolution of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Lithoshpere, 2021(1): 1–22.
-
Zhang J, Cunningham D. 2012. Kilometer-scale refolded folds caused by strike-slip reversal and intraplate shortening in the Beishan region, China[J]. Tectonics, 31(3): 1–19.
-
Zhang J, Cunningham D, Qu J F, Zhang B H, Zhao H, Zheng R G, Niu P F, Wang Y N, Zhao S, Hui J. 2022b. Poly-phase accretionary, collisional and intraplate tectonism in the Langshan region of the Alxa Block, China: Unravelling the complex structural evolution of the southern Central Asian Orogenic Belt [J]. Gondwana Research, 105(5): 25–50.
-
Zhang J, Li J Y, Xiao W X, Wang Y N, Qi W H. 2013a. Kinematics and geochronology of multistage ductile deformation along the eastern Alxa block, NW China: New constraints on the relation‐ ship between the North China Plate and the Alxa block[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 57(12): 38–57
-
Zhang J, Qu J F, Zhang B H, Zhao H, Zheng R G, Liu J F, Hui J, Niu P F, Yun L, Zhao S, Zhang Y P. 2022a. Determination of an intracontinental transform system along the southern Central Asian Orogenic Belt in the latest Paleozoic[J]. American Journal of Science, 322(7): 851–897.
-
Zhang J, Wang Y N, Qu J F, Zhang B H, Zhao H, Yun L, Li T Y, Niu P F, Nie F J, Hui J, Zhang Y P. 2020. Mesozoic intracontinental deformation of the Alxa Block in the middle part of Central Asian Orogenic Belt: A review[J]. International Geological Review, 63(11/12): 1490–1520.
-
Zhang J, Zhang B, Zhao H. 2016a. Timing of amalgamation of the Alxa Block and the North China Block: Constraints based on detrital zircon U – Pb ages and sedimentologic and structural evidence[J]. Tectonophysics 668/669(2): 65–81.
-
Zhang J, Zhang Y P, Xiao W X, Wang Y N, Zhang B H. 2015b. Linking the Alxa Terrane to the eastern Gondwana during the Early Paleozoic: Constraints from detrital zircon U-Pb ages and Cambrian sedimentary records[J]. Gondwana Research, 28(3): 1168–1182.
-
Zhang J J, Wang T, Castro A, Zhang L, Shi X J, Tong Y, Zhang Z C, Guo L, Yang Q D, Laccheri L M. 2016b. Multiple mixing and hybridization from magma source to final emplacement in the Permian Yamatu pluton, the northern Alxa Block, China[J]. Journal of Petrology, 57(5): 933–979.
-
Zhang J J, Wang T, Zhang L, Tong Y, Zhang Z C, Shi X J, Guo L, Huang H, Yang Q D, Huang W, Zhao J X, Ye K, Hou J Y. 2015a. Tracking deep crust by zircon xenocrysts within igneous rocks from the northern Alxa, China: Constraints on the southern boundary of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 108(15): 150–169.
-
Zhang J X, Gong J H, Yu S Y, Li H K, Hou K J. 2013b. Neoarchean-Paleoproterozoic multiple tectonothermal events in the western Alxa block, North China Craton and their geological implication: Evidence from zircon U-Pb ages and Hf isotopic composition[J]. Precambrian Research, 235(9): 36–57.
-
Zhang L Q, Zhang H F, Hawkesworth C, Luo B J, Yang H. 2021b. Mafic rocks from the southern Alxa block of Northwest China and its geodynamic evolution in the Paleozoic[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 178(3): 1–18.
-
Zhang W, Pease V, Meng Q P, Zheng R G, Wu T R, Chen Y, Gan L S. 2017. Age and petrogenesis of late Paleozoic granites from the northernmost Alxa region, northwest China, and implications for the tectonic evolution of the region[J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 106(1): 79–96.
-
Zhao G C, Sun M, Wildeb S A, Li S Z. 2005. Late Archean to Paleoproterozoic evolution of the North China Craton: Key issues revisited[J]. Precambrian Research, 136(2): 177–202.
-
Zhao P, Faure M, Chen Y, Shi G Z, Xu B. 2015. A new Triassic shortening-extrusion tectonic model for Central-Eastern Asia: Structural, geochronological and paleomagnetic investigations in the Xilamulun Fault (North China)[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 426(9): 46–57.
-
Zhao H, Zhang J, Qu J F, Zhang B H, Niu P F, Hui J, Zhang Y P. 2022. Geometry, kinematics and chronology of the Yabrai shear zone in the Alxa Block: Constraints on the late Paleozoic dextral shear system in the southern margin of the Central Asian orogenic belt[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 158(104575): 1–23.
-
Zhao X C, Liu C Y, Wang J Q, Zhang S H, Guan Y Z. 2020. Geochemistry, geochronology and Hf isotope of granitoids in the northern Alxa region: Implications for the Late Paleozoic tectonic evolution of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 11(5): 1711–1725.
-
Zheng R G, Li J Y, Xiao W J, Wang L J. 2018. A new ophiolitic mélange containing boninitic blocks in Alxa region: Implications for Permian subduction events in southern CAOB[J]. Geosience Frontier, 9(5): 1355–1367.
-
Zheng R G, Li J Y, Zhang J, Xiao W J, Li Y. 2019a. Early Carboniferous high Ba–Sr granitoid in southern Langshan of northeastern Alxa: Implications for accretionary tectonics along the southern Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica (English Edition), 93(4): 820–844.
-
Zheng R G, Li J Y, Zhang J. 2022. Juvenile Hafnium isotopic compositions recording a late Carboniferous – Early Triassic retreating subduction in the southern Central Asian Orogenic Belt: A case study from the southern Alxa[J]. Geological Society of American Bulletin, 134(5/6): 1375–1396.
-
Zheng R G, Wu T R, Zhang W, Xu C, Meng Q P, Zhang Z Y. 2014. Late Paleozoic subduction system in the northern margin of the Alxa block, Altaids: Geochronological and geochemical evidences from ophiolites[J]. Gondwana Research, 25(2): 842–858.
-
Zheng R G, Zhang J, Xiao W J. 2019b. Association of Permian gabbro and granite in the Langshan, southern Central Asian Orogenic Belt: Age, Origin, and tectonic implications[J]. Lithos, 348/349 (12): 1–17.
-
Zheng Y D, Wang S, Wang Y. 1991. An enornous thrust nappe and extensional metamorphic core complex newly discovered in Sino-Mongolian boundary area[J]. Science in China (Series B), 34 (9): 1145–1152.
-
Zheng Y D, Zhang Q. 1994. The Yagan Metamorphic Core Complex and extensional detachment fault in Inner Mangolia, China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica (English Edition), 7(2): 125–135.
-
Zhou Y Z, Han B F, Zhang B, Xu Z, Ren R, Li X W, Su L. 2012. The Yingba shear zone on the Sino-Mongolian border: Southwestern extension of the Zuunbayan Fault from Mongolia to China and implications for Late Mesozoic intracontinental extension in Eastern Asia[J]. Tectonophysics, 574/575(12): 118 –132.
-
崔骁, 王根厚, 王振义, 刘得文, 雷聪聪, 唐宇 . 2019. 内蒙额济纳旗霍布哈尔地区构造片岩带的发现及其构造意义[J]. 矿物岩石, 39(2): 81–89.
-
丁燕云, 李占奎 . 1999. 银根—额济纳旗盆地航磁反映的构造特征 [J]. 物探与化探, 23(3): 191–194.
-
宫江华, 张建新, 王宗起, 于胜尧, 王东升. 2018. 阿拉善地块晚奥陶世—石炭纪的构造演化历史——来自北大山地区多期岩浆-变质-变形事件的约束[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 37(5): 771–798.
-
公王斌, 胡建民, 吴素娟, 刘洋, 赵远方. 2017. 内蒙古狼山左行走滑韧性剪切带变形特征、时间及意义[J]. 地学前缘, 24(3): 263 –275.
-
关晶. 2010. 内蒙古阿拉善右旗塔木素地区阿尔嘎顺韧性剪切带研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京).
-
韩宝福, 张臣, 赵磊, 任荣, 徐钊, 陈家富, 张磊, 周印章, 宋彪. 2010. 内蒙古西部呼伦陶勒盖地区花岗岩类的初步研究[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 29(6): 741–749.
-
赖新荣, 江思宏, 邱小平, 刘妍, 胡朋, 张万益 . 2007. 阿拉善北大山岩带海西期中酸性岩40Ar/39Ar 年龄及其地球化学特征[J]. 地质学报, 81(3): 370–380.
-
李玉宏, 杨高印, 卢进才, 肖通新, 魏建设, 刘宽厚 . 2010. 综合地球物理方法在内蒙古西部额济纳旗及邻区石炭系—二叠系解释中的应用[J]. 地质通报, 29(Z1): 374–383.
-
卢进才, 牛绍武, 魏建设, 姜亭, 王宝文, 余龙, 许海红. 2018. 银额盆地西部蒙额地 1 井二叠纪叶肢介的发现及其意义[J]. 地质通报, 37(1): 16–25.
-
牛鹏飞, 曲军峰, 张进, 张北航, 赵衡. 2022. 阿拉善地块东部早前寒武纪变质基底性质及归属[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 41(2): 446 –466.
-
冉皞, 张维杰, 刘治博. 2012. 内蒙古阿拉善右旗杭嘎勒晚二叠世二长花岗岩地球化学特征和 LA–ICP–MS 锆石 U–Pb 定年[J]. 地质通报, 31(10): 1565–1575.
-
史兴俊, 童英, 王涛, 张建军, 张招崇, 张磊, 郭磊, 曾涛, 耿建珍 . 2012. 内蒙古西部阿拉善地区哈里努登花岗岩 LA–ICP–MS 锆石 U–Pb 年龄和地球化学特征[J]. 地质通报, 31(5): 662 –670.
-
史兴俊, 张磊, 张辰光, 张建军, 丁自源, 张勇, 包峻帆, 周红升 . 2020. 阿拉善北部亚干地区花岗岩锆石年代学、地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 地球科学, 45(7): 2469–2484.
-
王文宝, 雷聪聪, 李刚, 李卫星, 丁海生, 马军, 闫振军. 2022. 内蒙古西北部望湖山韧性剪切带构造特征及其地质意义[J]. 地质学报, 96, doi: 10. 19762/j. cnki. dizhixuebao. 2023103.
-
王东升, 宫江华, 张建新, 于胜尧 . 2016. 阿拉善地块中元古代诺尔公群的构造变形特征[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 35(2): 306–320.
-
魏仙样, 卢进才, 魏建设, 许海红, 李岩. 2014. 内蒙古银额盆地居延海坳陷X井地层划分修正及其油气地质意义[J]. 地质通报, 33 (9): 1409–1416.
-
吴凤萍 . 2009. 内蒙古阿拉善右旗塔木素地区 NNE 向韧性剪切带研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京).
-
吴晓智, 王桂君, 郑民, 郑曼 . 2015. 雅布赖盆地构造演化与油气聚集[J]. 地质科学, 50(1): 74–87.
-
熊盛青, 周道卿, 丁燕云, 郭志宏, 李占奎, 梁秀娟, 肖梦楚, 段宏伟, 胡悦, 佟晶, 吴云, 闫红雨, 赵宏雷, 高珊, 张琦洁. 2020. 银额— 河西走廊盆地群油气远景评价图集[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1 –107.
-
徐旺 . 1999. 对潮水盆地油气勘探的思考[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 26 (1): 92–95.
-
杨振德, 潘行适, 杨易福. 1998. 阿拉善断块及邻区地质构造特征与矿产[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1–254.
-
张伟, 王金荣, 陈万峰, 翟新伟, 马锦龙. 2014. 阿拉善右旗地区晚石炭世埃达克岩的发现及其大地构造意义[J]. 高校地质学报, 20 (3): 378–387.
-
张文, 吴泰然, 冯继承, 郑荣国, 贺元凯. 2013. 阿拉善地块北缘古大洋闭合的时间制约: 来自乌力吉花岗岩体的证据[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 43(8): 1299–1311.
-
郑荣国, 吴泰然, 张文, 冯继承, 徐操, 孟庆鹏 . 2013. 张昭昱阿拉善地块北缘雅干花岗岩体地球化学、地质年代学及其对区域构造演化制约[J]. 岩石学报, 29(8): 2665–2675.
-
摘要
大型走滑双重构造是造山带中重要构造,它可以发育于造山带演化的不同阶段,同时也是陆内变形的重要方式。大型走滑双重构造的形成具有特殊的边界条件,在不同类型造山带演化过程中起到的作用也不一样,然而目前还缺少足够的认识。中亚造山带是全球显生宙规模最大的增生型造山带,大规模的走滑作用在该造山带的演化中起到了关键作用。目前在该造山带中段的阿拉善地区识别出了一个大型的近东西向的走滑双重构造,该双重构造由7~8条不同方向的次级韧性剪切带组成,东西长约500 km,南北宽约 350 km,面积约 200000 km2 。形成一个巨大的 S-C like构造,发育时间为古生代末期—早中生代,区域运动学性质为韧性右行走滑,单条剪切带的走滑位移10~60 km,累积走滑距离250~500 km。它是中亚造山带南缘晚古生代末期—早中生代巨型韧性剪切系统的一部分,也是古亚洲洋关闭后中亚造山带整体变形的一部分。该走滑双重构造分别连接了西侧天山以及东侧兴蒙造山带不同类型的走滑变形,它的形成与较热的岩石圈以及不均一的造山带组成有关,而走滑双重构造的作用也是造成造山带内部结构均一化的过程。结合造山带的类型,一般走滑双重构造多发生在增生型造山带,而碰撞型造山带一般由于较冷的岩石圈而相对缺乏此类构造。阿拉善大型走滑双重构造是中亚造山带中少有报道的大型构造,它是造山带不均一的物质组成、强烈的岩浆作用以及华北克拉通的阻挡而造成的应变集中所导致,它不仅是连接中亚造山带东西的枢纽,而且也是构建中亚造山带结构的重要约束。
Abstract
Large strike-slip duplexes are important structures in orogenic belts, which can develop in different evolution stages of orogenic belts and are also important ways of intracontinental deformation. The formation of large-scale strike-slip duplexes has special boundary conditions and plays different roles in the evolution of different types of orogenic belts. However, there is still a lack of sufficient understanding. The Central Asian Orogenic Belt is the largest accretionary orogenic belt in the Phanerozoic era in the world, and large-scale strike slipping has played a key role in the evolution of this orogenic belt. A large near east-west strike-slip duplex has recently been identified in the Alxa in the middle segment of the CAOB, which consists of 7-8 secondary ductile shear zones with different directions, with an overall east-west length of more than 500 km, a north-south width of 350 km, and an area of approximately 200000 km2 . This huge S-C like structure was developed from the end of Paleozoic to the early Mesozoic, and was characterized by ductile dextral strike-slipping regionally. The strike-slip displacement of a single shear zone ranges from 10 km and 60 km, and the cumulative displacement of this mega-duplex is between 250 and 500 km. It belongs to the late Paleozoic to early Mesozoic mega-ductile shear system along the southern margin of the CAOB, and represents the overall deformation of the CAOB after the final closure of the Paleo-Asian Ocean. The strike-slip duplex connects different types of strike-slip deformation in the Tianshan to the west and the Xingmeng orogenic belt to the east, and its formation is related to a hotter lithosphere and heterogeneous composition of the orogenic belt. The role of the strike-slip duplexes is also a process of homogenizing the internal structures of orogenic belts. Combined with the types of orogenic belts, strike-slip duplexes generally occur in accretionary orogenic belts, while collision orogenic belts are relatively lacking in such structures due to its cooler lithosphere. The large strike-slip duplex in the Alxa is a rarely reported large-scale structure in the CAOB. It is caused by the combined interplay among heterogeneous composition of the orogenic belt, strong magmatism and strain concentration caused by the blocking of the North China Craton. It is not only a hub connecting the east and west of the CAOB, but also an important constraint for constructing the structure of the CAOB.