摘要
在天津山岭子地区,深部地热流体的成因演化一直是学术界关注的焦点,直接关系着天津市山岭子地热田地热资源的可持续开发利用,对于推动天津地区乃至整个京津冀地区地热资源的合理开发利用有着重大意义。本文检测了研究区33组不同储层的地热流体水样,分析了地热流体中Sr2+ 浓度与87Sr/86Sr特征关系、锶同位素与水文地球化学组分含量以及氘氧的相关关系,并结合山岭子地热田的地质构造特征,对山岭子地热田深部热储流体的成因、补给来源、路径及混合作用进行了研究。结果表明:研究区热储流体的 Sr浓度和87Sr/86Sr值在平面上东南高西北低,即位于沧东断裂附近 Sr2+ 浓度和87Sr/86Sr值高,随着距沧东断裂的距离越远Sr2+ 浓度和87Sr/86Sr值越低;垂向上Sr2+ 浓度和87Sr/86Sr值随着热储层埋藏深度的增加而升高。研究区内地热流体由天津北部蓟县山区的大气降水入渗经过较远距离径流后补给形成的,位于沧东断裂附近的明化镇组、馆陶组、奥陶系和雾迷山组地热流体之间存在着水力联系,沧东断裂是地热流体运移的通道。研究区内地热流体的热储环境为半封闭性,存在一定水岩作用的古溶滤水。
Abstract
In the Tianjin Shanlingzi region, the genesis and evolution of deep geothermal fluids have been a focal point of academic attention, directly impacting the sustainable development and utilization of geothermal resources in the Shanlingzi geothermal field, Tianjin. This study analyzed water samples from 33 different reservoirs in the research area, examining the relationship between Sr2+ concentration and 87Sr/86Sr ratios in geothermal fluids, as well as the correlations between strontium isotopes and hydrogeochemical components and deuterium-oxygen isotope ratios. Combining these analyses with the geological structural characteristics of the Shanlingzi geothermal field, the study investigated the genesis, recharge sources, pathways, and mixing processes of deep geothermal reservoir fluids in the Shanlingzi geothermal field. The results indicate that Sr concentrations and 87Sr/86Sr ratios in the thermal reservoir fluids are higher in the southeast and lower in the northwest, with higher Sr2+ concentrations and 87Sr/86Sr ratios near the Cangdong Fault and decreasing values with increasing distance from the fault. Vertically, Sr2+ concentrations and 87Sr/86Sr ratios increase with the depth of the geothermal reservoir. The geothermal fluids within the research area are formed by atmospheric precipitation infiltration from the northern Jixian mountainous area of Tianjin, traveling over long distances before recharging. There is hydraulic connectivity between the Minghuazhen Formation, Guantao Formation, Ordovician System, and Wumishan Formation geothermal fluids near the Cangdong Fault, with the Cangdong Fault serving as a conduit for geothermal fluid migration. The geothermal reservoir environment in the research area is semi-closed, with ancient leached water exhibiting some degree of water-rock interaction.
0 引言
国内锶同位素研究兴起于 20 世纪 90 年代,最初利用在河流、大气降水等地表水和浅层地下水上。周炼等(1997)、赵继昌等(2003)、杨郧城等 (2007)、叶萍等(2008)、罗丹等(2019)利用 Sr2+ 浓度和87Sr/86Sr研究了地下水的来源、演化、水岩反应等。目前国内对于锶同位素在地下热水的研究越来越多,锶作为一种较重的稳定同位素,具有在自然作用下不发生显著分馏,且对水岩作用反应灵敏的特征(Cartwright et al.,2007;Luo et al.,2014;Oyuntsetseg et al.,2015),鉴于锶同位素的特性,其在地热系统中的应用也相对重视起来,赵平等(2003)、徐国芳和马致远(2013)、荆慧等(2015)利用 Sr2+ 含量及锶同位素比值87Sr/86Sr的关系,揭示深部地热流体赋存环境等。前人对天津市地热资源的研究做了很多有意义的工作,主要利用水文地球化学、氘氧同位素、14C同位素等对地热流体的补给来源和运移机制进行研究(高宝珠等,2009;张芬娜等,2015;杨吉龙等,2018;岳冬冬等,2020),而对热储储层之间的水力联系的相关研究较少。
鉴于此,本文以天津山岭子地热田地热流体为研究对象,首次通过水化学及锶同位素地球化学方法分析不同热储层水样,结合87Sr/86Sr 的特征,对地热流体的补给来源和各储层之间的水力联系进行研究,深化研究区地热流体的认识,以期能为研究区地热系统的综合研究提供借鉴,并对其可持续开发利用提供科学依据。
1 地热地质概况
本研究以天津断裂以东、沧东断裂以西和海河断裂以北为研究区,研究区位于Ⅱ级构造单元沧县隆起之Ⅲ级构造单元潘庄凸起上(图1)。区内已查明多个热储层,自上而下,依次发育新近系明化镇组、馆陶组、古生界奥陶系和蓟县系雾迷山组热储层(图2;李俊峰等,2008;李嫄嫄,2014;贾志等, 2015)。明化镇组热储层全区连续分布,馆陶组热储层在研究区西部缺失,奥陶系热储层仅在研究区南部分布,蓟县系雾迷山组热储层全区均有分布,各热储特征详见表1(李俊峰等,2008;李嫄嫄, 2014;贾志等,2015)。
2 样品采集与测试
在收集整理已有地热流体水化学和同位素数据的基础上,本研究于 2017 年 11 月份在山岭子地热田(主要位于东丽区和河东区)内采集了 33 个地热流体样品(图1)。锶同位素及水化学样品均用 500 ml聚乙烯瓶进行采集,在取样前先用蒸馏水进行了 3 次以上的清洗,在抽水取样前,充分抽水洗井,待取样井恢复稳定再进行抽水取样,用待采水样清洗取样瓶2~3次,再取满水样,排出水样瓶中空气,用石蜡封口,胶带密封,保证水样不与外界接触,贴好水样标签,填写送样单。第四系及地热流体地热水化学组分全分析,现场测试检测项目包括 pH 值、温度和总溶解性固体等,试验室内检测项目包括K+、Na+、Ca2+、Mg2+、NH4 +、Cl-、SO4 2-、HCO3-、NO3-、 F-等。锶同位素和13C 样品委托核工业北京地质研究院进行测试,其中87Sr/86Sr采用热表面电离质谱仪测试,仪器型号 Phoenix,测试精度为 2σ,实验室温度保持在 20℃,相对湿度为 30%。δ13C 采用气体同位素质谱仪测试,仪器型号 MAT-253,测试精度为 ±0.2‰,实验室温度保持在 24℃,相对湿度为 30%。地热全分析样品由国土资源部天津矿产资源监督检测中心测试,采用电感耦合等离子体光谱仪,仪器型号 Optima8300,相对测定误差为 1%。因测试时,Sr2+ 浓度未和87Sr/86Sr 同时测试,Sr2+ 浓度为补测的,所以测试 Sr2+ 浓度值的水样较少,不同热储层地热流体测试项目样品结果见表2。

图1研究区地质构造及地热流体取样位置图
1 —断裂;2—断裂带;3—第四系取样点及编号;4—地热流体取样点及编号;5—行政区;6—剖面线及编号
表1研究区热储层特征


图2A-A′地质剖面示意图
表2地热水化学特征

不同储层水样主要指标统计分析(表3):在第四系水中 pH 范围 8.27~8.50,均值 8.27,TDS 范围 519~650 mg/L,平均值 568.67 mg/L,87Sr/86Sr 范围 0.7091~0.7095,均值 0.7092;明化镇组地热流体中 pH 范围 7.66~8.50,均值 8.17,TDS 范围 482~1674 mg/L,平均值 1274.63 mg/L,87Sr/86Sr 为 0.7075~0.7116,均值 0.7094;馆陶组地热流体中 pH 范围 7.5~8.3,均值 7.95,TDS 范围 1066~1764 mg/L,平均值 1474.33 mg/L,87Sr/86Sr 范围 0.7094~0.7106,均值 0.7097;奥陶系地热流体中 pH 范围 7.53~8.19,均值 7.87,TDS 范围 1333~1767 mg/L,平均值 1562.27 mg/ L,87Sr/86Sr 范围 0.7113~0.7116,均值 0.7114;雾迷山组地热流体中 pH 范围 7~8.35,均值 7.81,TDS 范围 332.8~2196.1 mg/L,平均值 1644.63 mg/L,87Sr/86Sr 范围 0.7095~0.7118,均值 0.7113。随着热储埋深的加深,pH由碱性趋于弱碱性,TDS和87Sr/86Sr逐渐升高,但奥陶系和雾迷山组87Sr/86Sr 值相差不大。主要由于随着热储埋深的增加,地热流体循环深度增加,循环时间较长,地热流体与周围岩石的水岩作用较强。
表3不同储层水样主要指标统计

3 讨论
3.1 锶同位素的演化特征
地热流体样点Sr2+ 含量和87Sr/86Sr值的差别与地热流体流经路径的岩性和水-岩相互作用有关(叶萍等,2008)。由于锶在水文地球化学作用过程中不发生显著分馏,随着水-岩相互作用时间的延长,水体中 Sr2+ 含量逐渐增加,其同位素比值一般也与含水介质中溶解矿物的87Sr/86Sr值相似,且在同一含水岩层中地热流体年龄越老,岩层中的 Rb 经过 β-衰变,会生成更多的87Sr(刘英俊等,1984;马致远等,2015),因此87Sr/86Sr 值会越大,所以 Sr2+浓度和87Sr/86Sr值也可有效地反映水-岩相互作用强度和反应时间,即热水滞留时间。
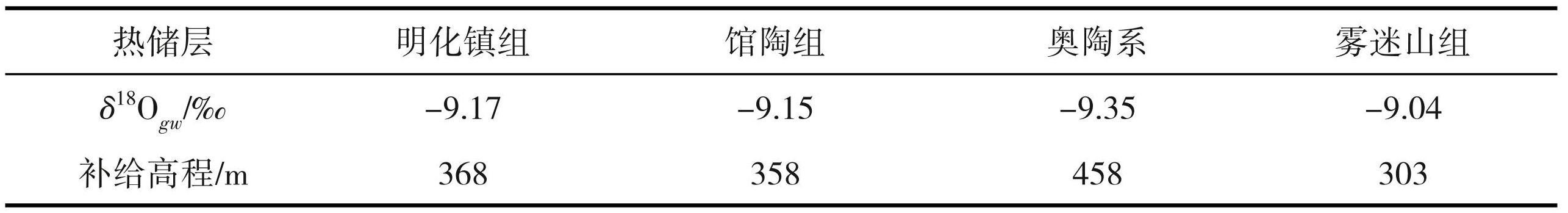
通过地热流体水样点分析,研究区内各储层地热流体的Sr2+ 浓度和87Sr/86Sr值均表现为东南高西北低(图3),即位于沧东断裂附近Sr2+ 浓度和87Sr/86Sr值高,随着距沧东断裂的距离越远 Sr2+ 浓度和87Sr/86Sr 值越低,表现出明显的时间累积效应;垂向上明化镇组地热流体的87Sr/86Sr 值随着热储层埋藏深度的增加而升高(图4),其他热储层地热流体的Sr2+ 浓度和87Sr/86Sr 值随着热储层埋藏深度的增加变化不明显。
地热流体中锶主要来源于硅酸盐、碳酸盐和硫酸盐等矿物的溶解,不同岩石组分具有其特定的87Sr/86Sr值,不同储层的地热流体因为流经不同岩石具有不同的87Sr/86Sr 值,因此87Sr/86Sr 值可以说明地热流体源于何处,与何种矿物岩石进行了水岩反应(马致远等,2015)。由表2可以看出,随着热储层深度的增加87Sr/86Sr值逐渐增大,说明埋藏越深地热流体循环越慢。研究区内明化镇组地热流体的87Sr/86Sr值(0.7075~0.7116)普遍低于 0.7085,接近碳酸盐岩地层的87Sr/86Sr值,推断是受水岩作用的影响,地热流体流经 Rb含量较高的新近系砂岩,使得地热流体中87Sr含量增大,从而87Sr/86Sr值变大;馆陶组、奥陶系和雾迷山组地热流体87Sr/86Sr值相对较高 (0.7083~0.7118),而 Sr 浓度较低,与硅铝酸盐类水高87Sr/86Sr值低Sr浓度特征相符。

图3研究区地热流体Sr2+ 含量(a)及87Sr/86Sr比值(b)等值线图
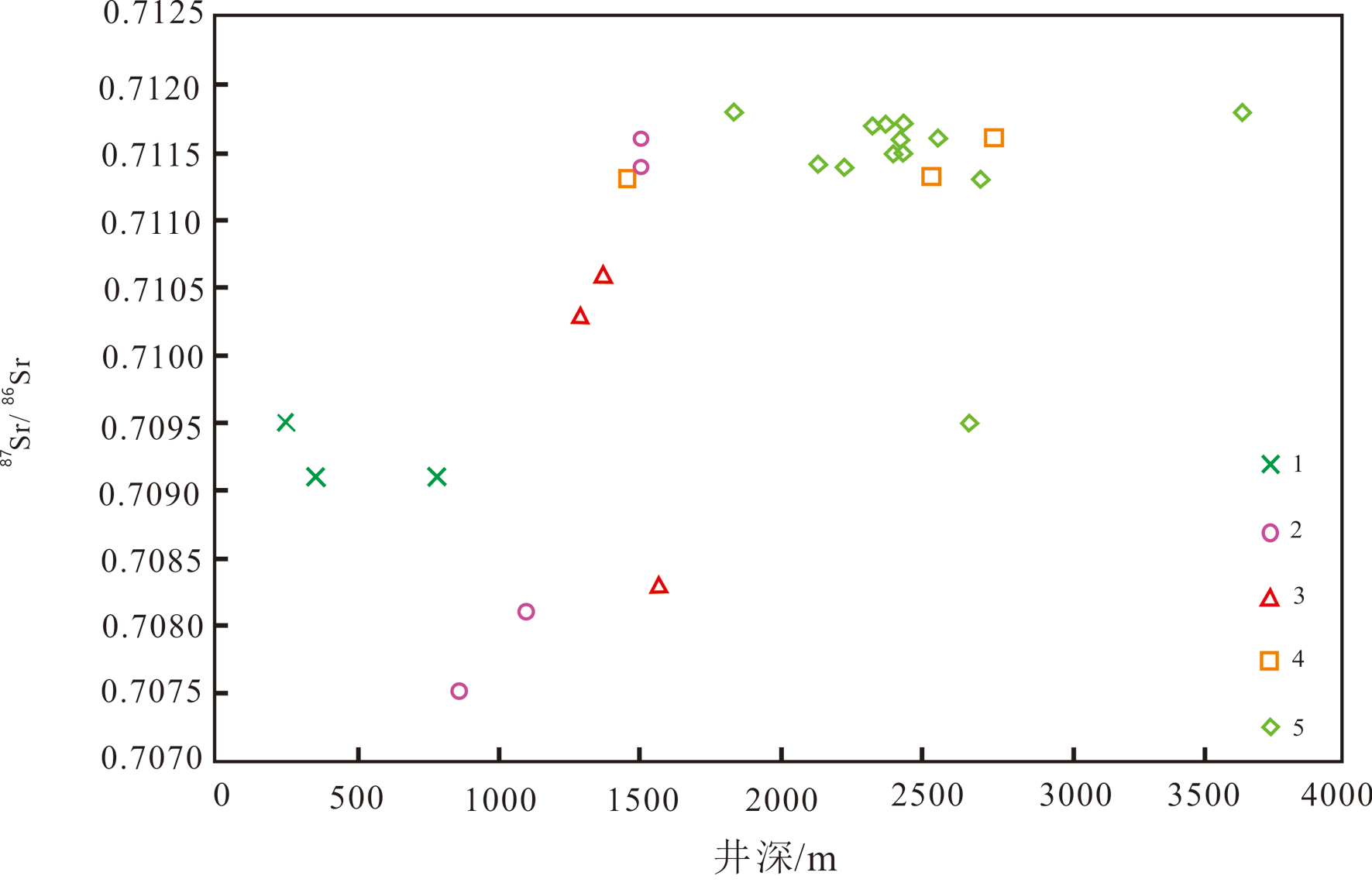
图4地热流体87Sr/86Sr与井深关系图
1 —第四系;2—明化镇组;3—馆陶组;4—奥陶系;5—雾迷山组
如图5所示,研究区地热流体样点以稳定的低 Sr 含量(0~2.73 mg/L)和较大差异的87Sr/86Sr 值 (0.7075~0.7118)(郑磊,2015)为特征,地热流体中锶比值变化呈以下规律:由西北向东南,地热流体锶比值沿水流方向由小到大,显示锶同位素的年代累计效应,说明地热流体的补给来源为北部山区。位于沧东断裂两侧的明化镇组 6号样点、馆陶组 14 号样点、奥陶系 17号样点和雾迷山组 23、27号样点以稳定的87Sr/86Sr 值和变化较大的 Sr2+ 含量为特征, 87Sr/86Sr 值的稳定性说明其有共同的补给源,但 Sr2+ 的差异说明了补给到滞留区水岩反应逐渐加强的渐变过程;而 Sr2+ 浓度变化不大,说明明化镇组、馆陶组、奥陶系和雾迷山组之间存在着水力联系,地热流体沿着沧东断裂运移。

图5地热流体87Sr/86Sr与Sr2+ 关系图(图中数字序号为样品编号)
a—地热流体87Sr/86Sr与Sr2+ 关系图;b—地热流体87Sr/86Sr与Sr2+ 关系图(图b为图a的比例尺放大)
1 —第四系;2—明化镇组;3—馆陶组;4—奥陶系;5—雾迷山组
3.2 对地热流体的补给和水流路径的指示意义
锶同位素与 Ca2+、Mg2+ 的关系可指示接受补给的水流路径和水岩反应过程(马致远等,2015;贾凤超等,2020;岳冬冬等,2023)。图6中馆陶组地热流体和奥陶系地热流体的Sr2+ /Ca2+ 均呈正相关的关系,但Sr/Ca值不同,说明馆陶组地热流体和奥陶系地热流体存在相似的热储环境和水-岩作用。相同87Sr/86Sr-Sr/Ca 的关系样点应赋存于相同的热储环境,图6b中奥陶系地热流体样点 15、17和雾迷山组地热流体样点 23重合,这 2个样点位于沧东断裂东西两侧,表明沧东断裂附近奥陶系和雾迷山组地热流体之间有一定的水力联系,说明研究区地表水在地质历史时期,或以地表地下径流或通过断裂对热水系统产生影响。同时也证明了沧东断裂对研究区各储层地热流体的形成、补给有主要影响。馆陶组地热流体 Ca2+ 浓度大于奥陶系地热流体,而锶比值馆陶组地热流体小于奥陶系地热流体,这与 Sr、Ca类质同象作用有关,馆陶组地热流体 Sr/Ca 比值大于奥陶系地热流体,说明馆陶组接受奥陶系地热流体的补给,这与高宝珠等(2009)研究的结论是一致的。
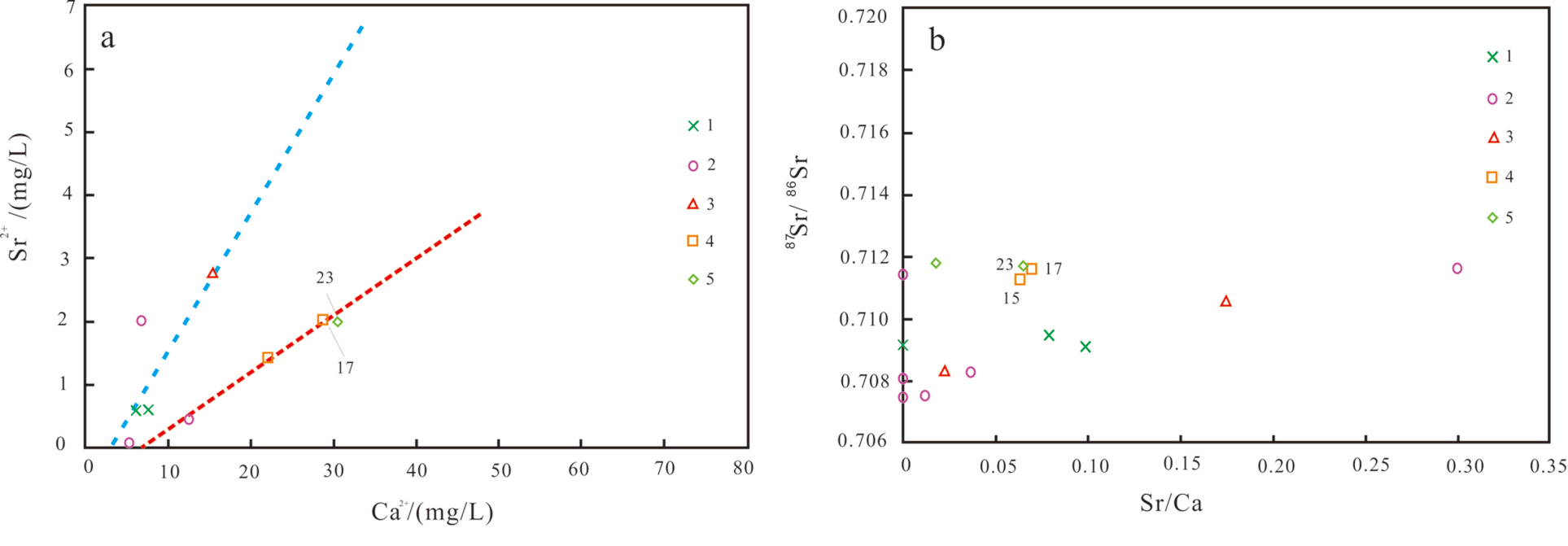
图6研究区各热储层地热流体Sr2+ 与Ca2+ 关系图(图中数字序号为样品编号)
a—锶同位素与Ca2 关系图;b—(87Sr/86Sr)-(Sr/Ca)的关系样点图
1 —第四系;2—明化镇组;3—馆陶组;4—奥陶系;5—雾迷山组
地热流体中 Sr2+ 浓度随着径流路径和径流时间的增长而增加,从补给区到滞留区Sr2+ /Ca2+ 、Sr2+ /Mg2+ 值也逐渐升高,混入作用使TDS值变高,但Sr2+ /Ca2+、 Sr2+ /Mg2+ 值基本不发生变化。Sr2+ /Ca2+、Sr2+ /Mg2+ 值可以还原岩溶水体天然径流条件。如图7所示,沧东断裂附近的奥陶系 17号样点和雾迷山组 23号样点重合,说明其补给来源相同,而其他远离沧东断裂的地热流体Sr/Ca、TDS无交集,说明其补给来源不同。
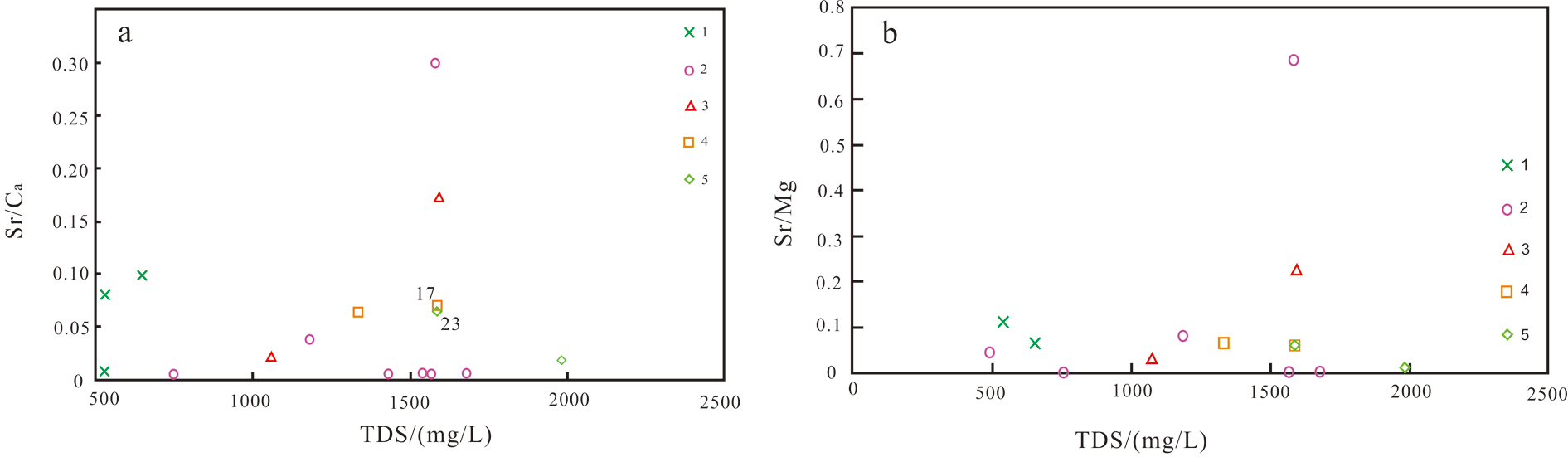
图7研究区各热储层地热流体Sr/Ca-TDS(a)及Sr/Mg-TDS(b)关系图(图中数字序号为样品编号)
1 —第四系;2—明化镇组;3—馆陶组;4—奥陶系;5—雾迷山组
在天津平原区,地热的形成与构造的活动性呈正相关关系,山岭子地热田位于沧东断裂与海河断裂交汇点,该带岩石更为破碎,裂隙密布,是地下热水的良好通道和赋存空间(靳宝珍,2005)。在沧东断裂附近馆陶组、奥陶系和雾迷山组地热流体存在着水力联系,进一步说明了断裂构造对地热的储存和运移起着控制性作用,在上覆热储盖层条件下,构造交汇或开启性断裂部位都可形成一定规模的带状热储并沿断裂对其他热储进行补给。
理论上大气降水的稳定同位素 δD 和 δ18O 随着降水高度高程的增大而减小,即具有高程效应。利用大气降水同位素的这种变化规律可确定地热流体的补给区和补给高程。地热流体补给高程的计算公式为:
(1)
式(1)中:H为地热流体补给高程(m);h为取样点地面高程(3 m);δ18Or为参考点水样 δ18O(取平均值-8.44‰);δ18Ogw 为取样点地热流体的 δ18O 值 (‰);grad18Or为雨水18O的高程梯度值(‰/100 m)。
参考中国华北地区降水 δ18O 的高程效应, gradδ18OVSMOW 取-0.2‰/100 m(Liu et al.,2009)。以天津南部平原区第四系浅层地下水为参考点,其 δ18Or 值选取第四系浅层地下水水样的平均值-8.44‰(表4)。δ18Ogw值选取各热储层地热流体样的平均值及计算的各热储层的地热流体的补给高程见表5。
表4各热储层地热流体的δ18O
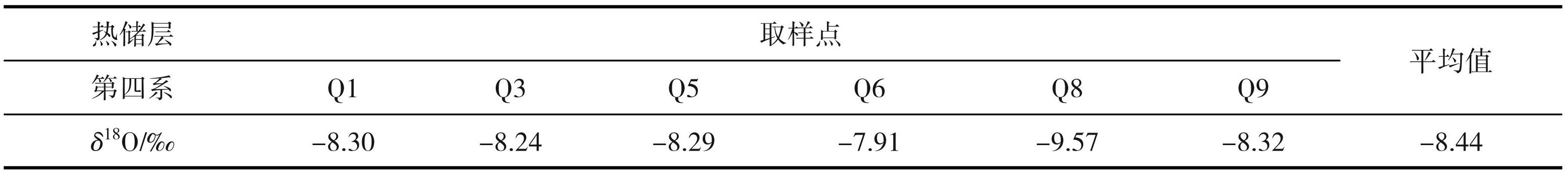
表5各热储层地热流体的δ18O及其补给高程
结合周边地形资料分析,补给高程与天津北部的蓟县山区高程相同,推测南部平原区地热流体是由天津北部蓟县山区的大气降水入渗经过较远距离径流后补给形成的。
锶比值反映水岩反应的过程,δ18O 反映水岩反应的程度。其关系完整地描述了水岩反应的类型,如图8所示,研究区内地热流体的热储环境为半封闭性,存在一定水岩作用的古溶滤水。地表水样点和第四系水样点沿大气降水线分布(靳宝珍, 2015①),说明其接受大气降水补给;研究区内各热储层地热流体样点分布于大气降水线下方(图9),有轻微的δ18O漂移,呈现了补给区的特征,说明受大气降水的补给,氢氧同位素支持了大气降水补给的结论(宋美钰等,2018;景营利等,2023)。
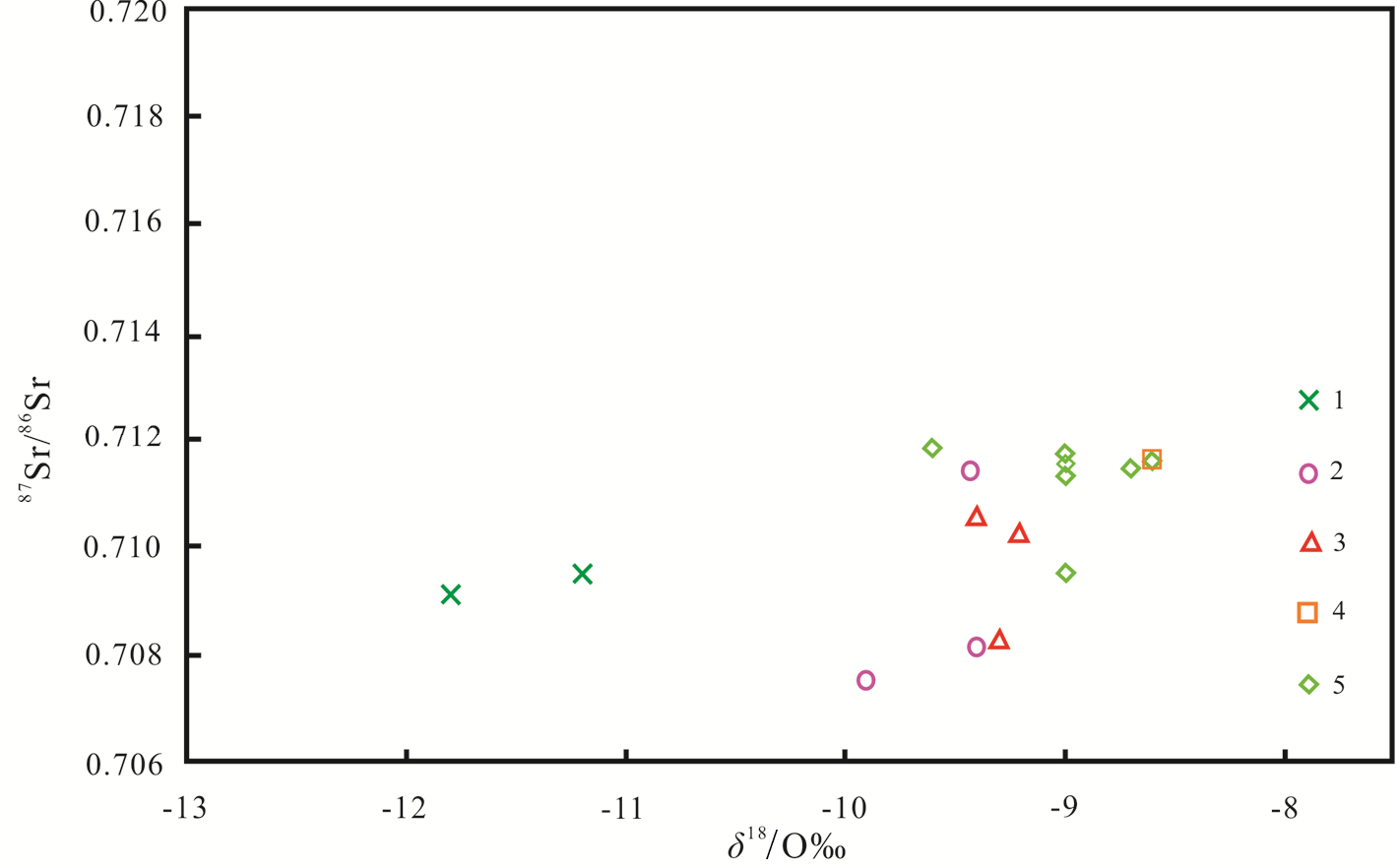
图8研究区热储流体87Sr/86Sr-δ18O关系图
1 —第四系;2—明化镇组;3—馆陶组;4—奥陶系;5—雾迷山组
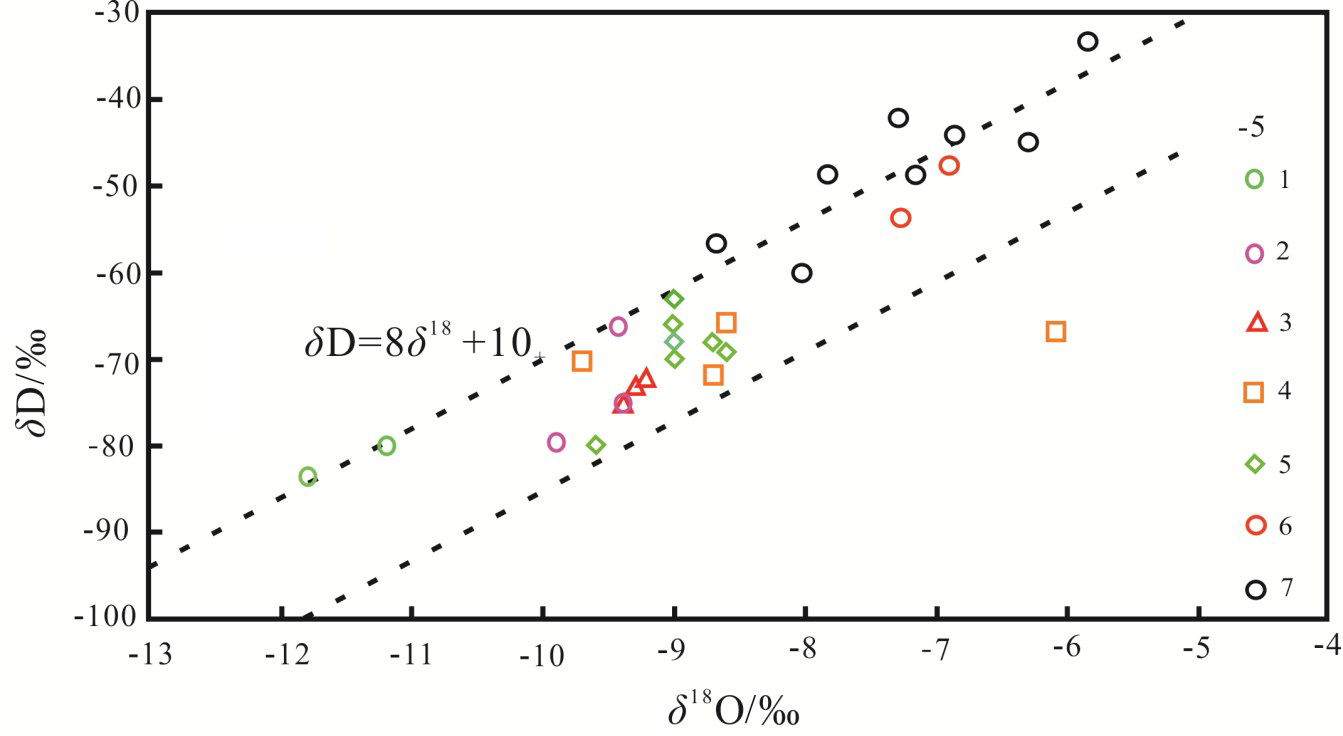
图9研究区热储流体δD-δ18O关系图
1 —第四系;2—明化镇组;3—馆陶组;4—奥陶系;5—雾迷山组;6—地表水;7—雨水
4 结论
(1)研究区各热储地热流体的Sr浓度和87Sr/86Sr 值在平面上东南高西北低,即位于沧东断裂附近 Sr2+ 浓度和87Sr/86Sr 值高,随着距沧东断裂的距离越远 Sr2+ 浓度和87Sr/86Sr 值越低;垂向上明化镇组地热流体Sr2+ 浓度和87Sr/86Sr值随着热储层埋藏深度的增加而升高。
(2)研究区内地热流体是由天津北部蓟县山区的大气降水入渗经过较远距离径流后形成的,地热流体的补给来源主要为大气降水入渗补给。
(3)沧东断裂是地热流体运移的主要通道,位于沧东断裂附近的明化镇组、馆陶组、奥陶系和雾迷山组地热流体之间存在着水力联系,深层地热流体与浅层地热流体有较强的混合作用。
(4)通过锶同位素的研究,研究区内地热流体的热储环境为半封闭性,存在一定水岩作用的古溶滤水。
注释
① 靳宝珍.2015. 天津市地热资源成矿规律调查与研究2012年度专题阶段成果报告[R]. 天津:天津地热勘查开发设计院.













